Question
Biomagnification factor, BMF, can be defined as the concentration of a chemical, X, in a predator, relative to the concentration found in its prey.
$\mathrm{BMF}=\frac{[\mathrm{X}]_{\text {predator }}}{[\mathrm{X}]_{\text {prey }}}$, where $[\mathrm{X}]=(\mu \mathrm{g} \mathrm{X}$ per kg body weight $)$
[Franklin, J., 2015. How reliable are field-derived biomagnification factors and trophic magnification factors as indicators of bioaccumulation potential? Conclusions from a case study on per-and polyfluoroalkyl substances. Available at: https://setac.onlinelibrary.wiley.com/doi/full/10.1002/ieam.1642.]
a. Calculate the BMF if a $120 \mathrm{~kg}$ shark consumes 1000 mackerel in one year. Each mackerel weighs $1 \mathrm{~kg}$ on average. The $[\mathrm{X}]_{\text {mackerel }}=0.3 \mu \mathrm{g} \mathrm{X}$ per $\mathrm{kg}$ body weight. Assume chemical X remains in the shark’s body for two years.
b. Suggest, with a reason, if fat-soluble or water-soluble xenobiotics would have a larger BMF.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. $« 0.3 \mu \mathrm{g} \times 2000=» 600 \ll \mu \mathrm{g} X »$
$$
\text { « } \frac{\frac{600 \mu \mathrm{g}}{120 \mathrm{~kg}}}{0.3 \mu \mathrm{g} \mathrm{kg}^{-1}}=» 17
$$
Award [2] for correct final answer.
M2 may also be correctly expressed to 1 SF.
b. fat-soluble $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ pass through lipid membranes/accumulate in cells/fatty tissues OR
fat-soluble AND less easily excreted $/$ metabolized
Accept “water-soluble” only if an organometallic-protein interaction is mentioned.
Question
Starch is a natural polymer of glucose.
a. Draw the structure of the repeating unit of starch and state the type of linkage formed between these units.
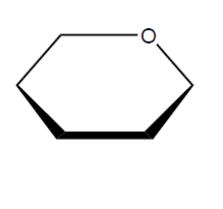
Type of linkage:
b. Formulate the equation for the complete hydrolysis of a starch molecule, $\left(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{10} \mathrm{O}_5\right)_n$.
c. Calculate the energy released, in $\mathrm{kJ} \mathrm{g}^{-1}$, when $3.49 \mathrm{~g}$ of starch are completely combusted in a calorimeter, increasing the temperature of $975 \mathrm{~g}$ of water from $21.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$ to $36.0^{\circ} \mathrm{C}$. Use section 1 of the data booklet.
d. Explain how the inclusion of starch in plastics makes them biodegradable.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a.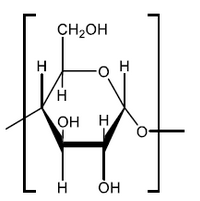
continuation bonds $A N D$-O- attached to just one end $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ both $\mathrm{H}$-atoms on end carbons must be on the same side [ $\boldsymbol{C}$ ]
Note: Square brackets not required.
Ignore ” $n$ ” if given.
Mark may be awarded if a polymer is shown but with the repeating unit clearly identified.
Type of linkage:
glycosidic [ $\checkmark]$
Note: Accept “ether”.
b. $\left(\mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{10} \mathrm{O}_5\right)_n(\mathrm{~s})+n \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l}) \rightarrow n \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_6(\mathrm{aq})[/]$
Note: Accept ” $(n-1) \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}$ “.
Do not award mark if ” $n$ ” not included.
c. $q=« m c \Delta T=975 \mathrm{~g} \times 4.18 \mathrm{~J} \mathrm{~g}^{-1} \mathrm{~K}^{-1} \times 15.0 \mathrm{~K}=» 61100 \ll \mathrm{J} » / 61.1$ «J»] [ «heat per gram $=\frac{61.1 \mathrm{~kJ}}{3.49 \mathrm{~g}}=» 17.5$ «J g g $^{-1} »[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Award [2] for correct final answer.
d. Any two of:
carbohydrate grains swell/break plastic into smaller pieces $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
inclusion of carbohydrate makes the plastic more hydrophilic/water soluble $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
carbohydrates are broken down/hydrolysed/digested by bacteria/micro-organisms $[\boldsymbol{}]$
plastic becomes more accessible to bacteria as holes/channels are created in it $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
«presence of» carbohydrate weakens intermolecular/London/dispersion forces between polymer chains in the plastic [ $\boldsymbol{J}$ ]
Note: Accept “starch” for “carbohydrate” throughout. Do not accept carbohydrates are broken down/hydrolyzed.
Question
Proteins have structural or enzyme functions.
Oil spills are a major environmental problem.
a(i)Some proteins form an a-helix. State the name of another secondary protein structure.
a(ii) Compare and contrast the bonding responsible for the two secondary structures.
One similarity:
One difference:
b. Explain why an increase in temperature reduces the rate of an enzyme-catalyzed reaction.
c(i)Suggest two reasons why oil decomposes faster at the surface of the ocean than at greater depth.
c(ii) $i l$ spills can be treated with an enzyme mixture to speed up decomposition.
Outline one factor to be considered when assessing the greenness of an enzyme mixture.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a(i) $\beta /$ beta pleated/sheet $[\boldsymbol{U}$ ]
a(ii) One similarity:
hydrogen bonding
OR
attractions between $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ and $\mathrm{N}-\mathrm{H}[\boldsymbol{U}]$
One difference:
$\alpha$-helix has hydrogen bonds between amino acid residues that are closer than $\beta$-pleated sheet
OR
H-bonds in a-helix parallel to helix axis AND perpendicular to sheet in $\beta$-pleated sheet
OR
a-helix has one strand $A N D \beta$-pleated sheet has two «or more» strands
OR
a-helix is more elastic «since $\mathrm{H}$-bonds can be broken easily» AND $\beta$-pleated sheet is less elastic «since $\mathrm{H}$-bonds are difficult to break» [ $\boldsymbol{\text { ] }}$
Note: Accept a diagram which shows hydrogen bonding between $\mathrm{O}$ of $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ and $\mathrm{H}$ of $\mathrm{NH}$ groups for $\mathrm{M1}$.
Accept “between carbonyl/amido/amide/carboxamide” but not “between amino/amine” for M1.
b. enzyme denatured/loss of 3-D structure/conformational change
OR
«interactions responsible for» tertiary/quaternary structures altered $[\boldsymbol{C}]$
shape of active site changes
OR
fewer substrate molecules fit into active sites $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
c(i)Any two of:
surface water is warmer «so faster reaction rate»/more light/energy from the sun [ $\boldsymbol{C}]$
more oxygen «for aerobic bacteria/oxidation of oil» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
greater surface area $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
c(ii)Any one of:
non-hazardous/toxic to the environment/living organisms $[\boldsymbol{}]$
energy requirements «during production» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
quantity/type of waste produced «during production»
OR
atom economy [ $\boldsymbol{C}]$
safety of process $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Accept “use of solvents/toxic materials “during production»”.
Do not accept “more steps involved”.
Question
Vitamins are organic compounds essential in small amounts.
a. State the name of one functional group common to all three vitamins shown in section 35 of the data booklet.
b. Explain the biomagnification of the pesticide DDT.
c. Explain why maltose, $\mathrm{C}_{12} \mathrm{H}_{22} \mathrm{O}_{11}$, is soluble in water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. hydroxyl
NOTE: Accept “hydroxy” but not “hydroxide”.
Accept “alkenyl”.
Do not accept formula.
b. accumulates in fat/tissues/living organisms
OR
cannot be metabolized/does not break down «in living organisms»
OR
not excreted / excreted «very» slowly
passes «unchanged» up the food chain
OR
increased concentration as one species feeds on another «up the food chain»
NOTE: Accept “lipids” for “fat”.
c. «solubility depends on forming many» $\mathrm{H}$-bonds with water
maltose has many hydroxyl/OH/oxygen atom/O «and forms many $\mathrm{H}$-bonds»
NOTE: Reference to “with water” required.
Accept “hydroxy” for “hydroxyl” but not “hydroxide/OH”
Reference to many/several $\mathrm{OH}$ groups/O atoms required for $M 2$.
Question
Enzymes are biological catalysts.
a. The graph shows the relationship between the temperature and the rate of an enzyme-catalysed reaction.
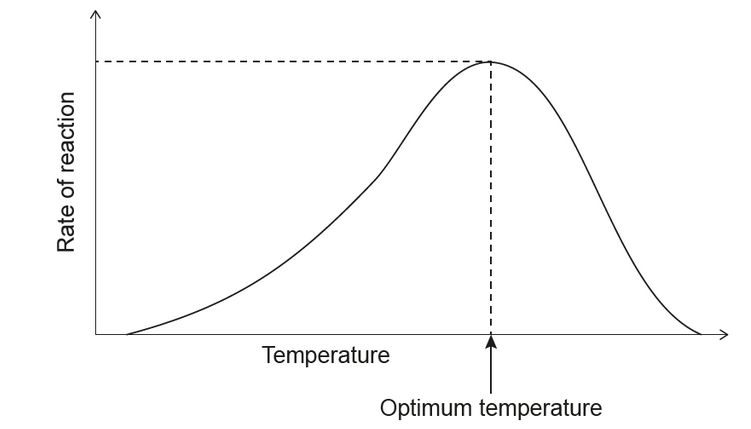
State one reason for the decrease in rate above the optimum temperature.
b. Explain why a change in $\mathrm{pH}$ affects the tertiary structure of an enzyme in solution.
c. State one use of enzymes in reducing environmental problems.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. enzyme denatures
OR
change of conformation/shape of active site
OR
substrate cannot bind to active site/binds less efficiently
NOTE: Accept “change in structure” or “substrate doesn’t fitfits poorly into active site”
b. Any two of:
acidic/basic/ionizable/ $\mathrm{COOH} /$ carboxyl/ $\mathrm{NH}_2$ /amino groups in the $\mathrm{R}$ groups/side chains «react»
exchange/lose/gain protons/ $\mathrm{H}^{+}$
change in H-bonds/ionic interactions/intermolecular forces/London dispersion forces
NOTE: Do not accept “enzyme denatures” OR “change of conformation/tertiary structure” OR “substrate cannot bind to active site/binds less efficiently” as this was the answer to 8(a).
c. breakdown of oil spills/industrial/sewage waste/plastics
OR
production of alternate sources of energy «such as bio diesel»
OR
involve less toxic chemical pathway «in industry»
NOTE: Accept “«enzymes in» biological detergents can improve energy efficiency”.
Question
Dietary recommendations are made by scientists.
a. The formation of proteins from amino acids is an example of an anabolic reaction in the human body. State the source of energy for such a synthetic reaction.
b. Suggest why it is advisable for those living in northerly or southerly latitudes (that is away from the equator) to take vitamin D supplements during the winter.
c. Explain how a xenobiotic is biomagnified.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. catabolism «of food/nutrients»
OR
«cellular» respiration
Accept “ATP” but not “burning of food/nutrients”.
b. not enough sunlight/UV light «for synthesis of vitamin D in the skin»
c. cannot be metabolized/broken down
OR
not biodegradable
OR
accumulates in lipid/fat tissues
increased concentration as one species feeds on another «in the food chain»
Question
Enzymes are mainly globular proteins.
a. Describe the interaction responsible for the secondary structure of a protein.
b.i. Explain the action of an enzyme and state one of its limitations.

b.ii.Enzymes are widely used in washing detergents. Outline how they improve the efficiency of the process.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. hydrogen bonding
between $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ and $\mathrm{H}-\mathrm{N}$ «groups»
Accept a diagram which shows hydrogen bonding for M1 and which shows the interaction between $\mathrm{O}$ of $\mathrm{C}=\mathrm{O}$ and $\mathrm{H}$ of $\mathrm{NH}$ groups for M2.
Accept “between amido/amide/carboxamide” but not “between amino/amine” for M2.
b.i. Enzyme action:
Any two of:
substrate binds to active site
weakens bonds in substrate
lowers activation energy
OR
provides alternate pathway
increases rate of reaction
OR
acts as catalyst
substrate specific
Limitation:
Any one of:
temperature dependent
$\mathrm{pH}$ dependent
can be sensitive to heavy metal ions
sensitive to denaturation
can be inhibited
substrate specific
Accept “favourable orientation/conformation of the substrate “enforced by enzyme»” for M1.
Do not accept “substrate specific” as both an enzyme action and a limitation.
b.ii Any one of:
«increase rate of» hydrolyse/break down lipids/oils/fats/proteins
«wash at» lower temperature/consume less energy
Question
Chloroethene, C2H3Cl, is an important organic compound used to manufacture the polymer poly(chloroethene).
Draw the Lewis structure for chloroethene and predict the H–C–Cl bond angle.
Draw a section of poly(chloroethene) containing six carbon atoms.
Outline why the polymerization of alkenes is of economic importance and why the disposal of plastics is a problem.
Chloroethene can be converted to ethanol in two steps. For each step deduce an overall equation for the reaction taking place.
Step 1:
Step 2:
State the reagents and conditions necessary to prepare ethanoic acid from ethanol in the laboratory.
State an equation, including state symbols, for the reaction of ethanoic acid with water. Identify a Brønsted-Lowry acid in the equation and its conjugate base.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
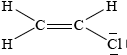 ;
;
Accept lines, dots or crosses for electron pairs.
Lone pairs required on chlorine.
(approximately) 120°;
Accept any bond angle in the range 113–120°.
 ;
;
Brackets not required for mark.
Continuation bonds from each carbon are required.
Cl atoms can be above or below carbon spine or alternating above and below.
plastics are cheap/versatile/a large industry / plastics have many uses / OWTTE;
plastics are not biodegradeable / plastics take up large amounts of space in landfill / pollution caused by burning of plastics / OWTTE;
Do not accept plastics cause litter.
Allow plastics don’t decompose quickly / OWTTE.
(i) Step 1:
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{CHCl}} + {{\text{H}}_2} \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{Cl}}\);
Step 2:
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{Cl}} + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ – } \to {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{OH}} + {\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ – }\);
Allow NaOH or NaCl etc. instead of OH– and Cl–.
Allow abbreviated formulas C2H3Cl, C2H5Cl, C2H5OH.
\({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{S}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{4}}}\)/\({{\text{H}}^ + }\)/acidified and \({\text{C}}{{\text{r}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}_{_{\text{7}}}^{2 – }\)/(potassium/sodium) dichromate;
Accept suitable oxidizing agents (e.g. KMnO4 etc.) but only with acid.
Ignore missing or incorrect oxidation states in reagents.
(heat under) reflux;
Second mark can be scored even if reagent is incorrect.
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ – }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}}\)
OR
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH(l)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ – }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_3}{{\text{O}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}}\)
OR
\({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{COOH(aq)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_3}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ – }{\text{(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}^ + }{\text{(aq)}}\)
correct equation;
state symbols and \( \rightleftharpoons \);
BL acid is \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH}}\) and cb is \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{CO}}{{\text{O}}^ – }\) / BL acid is \({{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{{\text{O}}^ + }\) and cb is \({{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}}\);
Examiners report
The main G2 comments on this question related to the inclusion of organic chemistry in Section A. It should be noted that ANY Topic can be asked in Section A of P2, and there is no set-formula in relation to question setting. Organic chemistry is an integral part of the IB SL Chemistry programme, and is covered in Topic 10 of the guide (12 hours in total). Hence, candidates should be adequately prepared for questions on this topic, even in Section A. In 3(a), the Lewis structure of chlorethene was generally drawn correctly, though the weaker candidates often omitted the lone pairs on the chlorine. The bond angle was usually predicted, although right angles and 109.5° were often given. Even some of the better candidates explained their choice of bond angle, based on the fact that the double bond occupies more space causing the HCCl bond angle to drop less than 120°.
Many candidates gave double bonds and some forgot to include continuation bonds.
The Aim 8 question in part (iii) was very well answered this session. Almost all candidates scored the disposal problem of plastics mark and many achieved the economics importance mark also.
In general (b) was very poorly answered, again showing a clear weakness in organic chemistry, which is an area of major concern. (i) was poorly done. Candidates who managed a correct reaction for the first step often used water instead of hydroxide ion for the second step.
In general (b) was very poorly answered, again showing a clear weakness in organic chemistry, which is an area of major concern. In (ii), candidates who mentioned dichromate(VI) or permanganate(VIII) often omitted the acid. In addition, reflux was often missing.
In general (b) was very poorly answered, again showing a clear weakness in organic chemistry, which is an area of major concern. In (iii), very few candidates scored all three marks here, even though the question itself was easy. The equation was often correct, but the equilibrium arrow was rarely given. Some candidates did not know the formula for ethanoic acid which was surprising.
Question
Petroleum (mineral oil) can be used either as a fuel or a chemical feedstock.
Name two fuels that are obtained from petroleum.
Describe one environmental problem that can result from the combustion of these fuels in the internal combustion engine and identify the specific combustion product responsible.
Plastic litter is an environmental problem that results from the use of petroleum as a chemical feedstock. Identify the property of plastics that is responsible for this.
One product that is made from crude oil is the chemical feedstock that can be used to synthesize commercial liquid-crystal displays. Discuss the properties that a substance must have to make it suitable for use as a liquid-crystal display.
d.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any two for [1]
petrol/gasoline
kerosene/paraffin/aviation fuel
diesel
fuel oil/gas oil
petroleum gas/refinery gas
a.
global warming;
carbon dioxide;
OR
air pollution;
carbon monoxide / particulates / oxides of nitrogen/NO/\({\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\) / \({\text{VO}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{s}}}\);
Accept oxides of sulphur/SO2.
OR
acid rain;
oxides of nitrogen/NO/\({\text{N}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{2}}}\);
Accept oxides of sulphur/SO2.
b.
slow decomposition / not biodegradeable;
c.
chemically stable;
liquid crystal phase over a suitable range of temperatures;
rapid switching speed;
d.
Examiners report
In part (a) a significant number of candidates named two fuels obtained from petroleum.
a.
A significant number of candidates described the environmental problem.
b.
The non-biodegradable property of plastics was stated correctly by many candidates.
c.
The properties of a material that made it suitable for use as a liquid crystal display demonstrated poor understanding by many candidates.
d.
Question
Glucose, C6H12O6, is a monosaccharide that our body can use as a source of energy.
Deduce the equation for the cellular respiration of glucose.
Calculate the energy, in kJ, produced from 15.0g of glucose if its enthalpy of combustion is −2803kJmol−1.
Glucose is the basic building block of starch which can be used to make bioplastics. Outline two advantages and two disadvantages of biodegradable plastics.
Two advantages:
Two disadvantages:
Bioplastics are broken down by enzyme catalysed reactions. Sketch a graph illustrating how the rate of this reaction varies with pH.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C6H12O6 (aq) + 6O2 (aq) → 6CO2 (aq) + 6H2O (l)
Accept equations for anaerobic respiration, such as C6H12O6 (aq) → 2C3H6O3 (aq)
Ignore ATP if added as a product.
\(n\left( {{{\rm{C}}_{\rm{6}}}{{\rm{H}}_{{\rm{12}}}}{{\rm{O}}_{\rm{6}}}} \right)\left\langle { = \frac{{15.0}}{{180.18}}} \right\rangle = 0.0833 \ll {\rm{mol}} \gg \)
«energy=0.0833×2803=»233«kJ»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
Accept -233«kJ».
Two advantages:
renewable resource
broken down/digested by bacteria or other organisms within a relatively short time/quickly
reduce «volume of» plastic waste/landfill
reduce use of petrochemicals
OR
reduce use of fossil fuels as hydrocarbon source
degrade into non-toxic products
Any two advantages for [2 max].
M2: reference must be made to time. Do not accept “biodegradable” (since stated in question).
Ignore any mention of cost.
Two disadvantages:
require use of land «for crop production»
increased use of fertilizers/pesticides «leading to pollution»
OR
eutrophication
might break down before end of use
release of methane/CH4/greenhouse gas «during degradation»
Any two disadvantages for [2 max].
Ignore any mention of cost.
typical curve as shown in example above √
Accept any curve with a single maximum (not just bell-shaped).
Ignore features such as pH values on a pH scale or a pH value at maximum (if given).
Do not penalize if curve does not touch the x-axis.
Question
Carbohydrates are energy-rich molecules which can be synthesized in some plant cells from inorganic compounds.
State the raw materials and source of energy used in the process described above.
The structures of two molecules, X and Y, are shown below.
(i) Justify why both these molecules are carbohydrates.
(ii) Distinguish between these molecules in terms of their functional groups.
Amylose is an unbranched polysaccharide composed of repeating units of glucose.
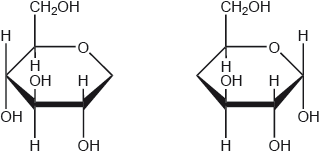
(i) Draw the structure of the repeating unit of amylose. Use section 34 of the data booklet.
(ii) Amylose is a major component of starch. Corn starch can be used to make replacements for plastics derived from oil, especially for packaging. Discuss one potential advantage and one disadvantage of this use of starch.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
CO2 AND H2O AND sun
Accept names.
Accept “sunlight/light/photons” instead of “sun”.
i
both have formula Cx(H2O)y
OR
both contain several OH/hydroxyl «groups» AND a C=O/carbonyl «group»
Accept “both have the formula CnH2nOn /empirical formula CH2O” but do not accept “both have same molecular formula/have formula C3H6O3”.
Accept “aldehyde or ketone” for “carbonyl”.
ii
Accept “alkyl” for “R”.
Accept “X: aldose/aldehyde AND Y: ketose/ketone”.
Accept “CO” for “C=O”.
i
continuation bonds AND open O on either but not both ends
Brackets are not necessary for the mark.
Do not accept β-isomer.
Mark may be awarded if a polymer is shown but with the repeating unit clearly identified.
3-D representation is not required.
ii
Advantage:
Any one of:
biodegradable / break down naturally/by bacteria
Do not accept just “decompose easily”.
compostable
does not contribute to land-fill
renewable/sustainable resource
starch grains swell AND help break up plastic
lower greenhouse gas emissions
uses less fossil fuels than traditional plastics
less energy needed for production
Disadvantage:
Any one of:
land use «affects biodiversity/loss of habitat»
growing corn for plastics instead of food
«starch» breakdown can increase acidity of soil/compost
«starch» breakdown can produce methane «especially when buried»
sensitive to moisture/bacteria/acidic foods
«bioplastics sometimes» degrade quickly/before end of use
cannot be reused
poor mechanical strength
eutrophication
increased use of fertilizers/pesticides/phosphorus/nitrogen «has negative environmental effects»
Ignore any reference to cost.
Accept “prone to site explosions/fires” or “low heat resistance” for disadvantage.
Only award [1 max] if the same example is used for the advantage and disadvantage.
Question
Sugars exist in both straight chain and ring forms.
Biodegradable plastics produced from starch present one solution to the environmental problem created by the use of large quantities of plastics.
Deduce the straight chain structure of ribose from its ring structure drawn in section 34 of the data booklet.
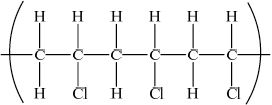
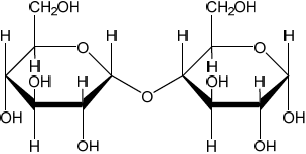
Using the partial structure given, complete the structural formula of the molecule formed from the condensation of two cyclic \(\alpha \)-glucose molecules.
Constructing models that allow visualizations of the stereochemistry of carbohydrates is essential to understand their structural roles in cells.
Describe how Haworth projections help focus on the position of attached groups.
State one advantage of starch based polymers besides being biodegradable.
Biodegradable boxes made from polylactic acid, PLA, disintegrate when exposed to water.
State the formula of the product formed when water reacts with PLA.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
All OH groups must be on the same side.
Accept structures with chiral carbon atoms shown as C or C* instead of crosses.
[1 mark]
Accept –O– in a straight line provided both H’s are above the plane.
[1 mark]
«allow» 3-D perspective of structures «of cyclic monosaccharide molecules»
OR
«show» cis/same side arrangement of «attached» groups
OR
«show» trans/opposite side arrangement of «attached» groups
OR
«make» carbon and hydrogen implicit
[1 mark]
abundant/renewable/allows use of «local» vegetation
OR
less use of fossil fuel/oil based plastics
OR
air permeable/better breathing of products
OR
«can be» mixed/blended with synthetic polymers
Do not accept answers related to biodegradable examples.
Ignore any reference to cost.
Accept “carbon neutral/do not contribute to global warming”.
Accept “require less energy to produce”.
Accept “do not produce toxic products”.
[1 mark]
HO–CH(CH3)–COOH/CH3CH(OH)COOH
Do not accept C3H6O3.
Do not accept OH–CH(CH3)–COOH.
[1 mark]
Question
Peptidase enzyme in the digestive system hydrolyses peptide bonds.
A tripeptide Ala-Asp-Lys was hydrolysed and electrophoresis of the mixture of the amino acids was carried out at a pH of 6.0. Refer to section 33 of the data booklet.
Identify the type of metabolic process that occurs in the hydrolysis of the peptide during digestion.
Identify the name of the amino acid that does not move under the influence of the applied voltage.
Deduce, giving a reason, which amino acid will develop closest to the negative electrode.
The breakdown of a dipeptide in the presence of peptidase was investigated between 18 °C and 43 °C. The results are shown below.
Comment on the rate of reaction at temperature X in terms of the enzyme’s active site.
The solubility of a vitamin depends on its structure.
Identify the vitamin given in section 35 of the data booklet that is the most soluble in water.
Pollution from heavy metal ions has become a health concern.
Outline how the presence of heavy metal ions decreases the action of enzymes.
Outline how lead ions could be removed from an individual suffering from lead poisoning.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
catabolism/catabolic
[1 mark]
alanine
Do not accept ala.
[1 mark]
Lys/lysine
pH «buffer» < pI «Lys»
OR
buffer more acidic than Lys «at isoelectric point»
OR
«Lys» exists as
OR
«Lys» charged positively/has +1/1+ «overall» charge «and moves to negative electrode»
Do not apply ECF from M1.
Accept converse argument.
Do not accept just “has H3N+ group” for M2 (as H3N+ is also present in zwitterion).
Do not penalize if COOH is given in the structure of lysine at pH 6 instead of COO–.
[2 marks]
highest frequency of successful collisions between active site and substrate
OR
highest frequency of collisions between active site and substrate with sufficient energy/\(E \geqslant {E_{\text{a}}}\) AND correct orientation/conformation
OR
optimal shape/conformation of the active site «that matches the substrate»
OR
best ability of the active site to bind «to the substrate»
Accept “number of collisions per unit time” for “frequency”.
Do not accept “all active sites are occupied”.
[1 mark]
ascorbic acid/vitamin C
[1 mark]
react/bind/chelate with enzyme
OR
disrupt ionic salt bridges
OR
affect shape of tertiary/quaternary structures
OR
precipitate enzymes
OR
break/disrupt disulfide bridges/bonds
Do not accept “changes shape of active site” by itself.
[1 mark]
«use of» host-guest chemistry
OR
chelation «therapy»
Accept specific medication/chelating agent such as EDTA, CaNa2 EDTA, succimer, D-penicillamine, dimercaprol.
[1 mark]
Question
Monosaccharides can combine to form disaccharides and polysaccharides.
Identify the functional groups which are present in only one structure of glucose.
Sucrose is a disaccharide formed from \(\alpha \)-glucose and β-fructose.
Deduce the structural formula of sucrose.
Starch is a constituent of many plastics. Suggest one reason for including starch in plastics.
Suggest one of the challenges scientists face when scaling up the synthesis of a new compound.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Only in straight chain form:
carbonyl
OR
aldehyde
Only in ring structure:
hemiacetal
Accept functional group abbreviations (eg, CHO etc.).
Accept “ether”.
[2 marks]
correct link between the two monosaccharides
Correct 1,4 beta link AND all bonds on the 2 carbons in the link required for mark.
Ignore any errors in the rest of the structure.
Penalize extra atoms on carbons in link.
[1 mark]
plastic «more» biodegradable/degrades into nontoxic products
OR
plastic can be produced using green technology/renewable resource
OR
reduces fossil fuel use/petrochemicals
OR
easily plasticized
OR
used to form thermoplasts
[1 mark]
minimize «negative» impact on environment
OR
minimize waste produced
OR
consider atom economy
OR
efficiency of synthetic process
OR
problems of side reactions/lower yields
OR
control temperature «inside large reactors»
OR
availability of starting/raw materials
OR
minimize energy costs
OR
value for money/cost effectiveness/cost of production
[1 mark]
Question
Lactose is a disaccharide formed by the condensation reaction of the monosaccharides galactose and glucose.
Describe what is meant by a condensation reaction.
Draw the structure of galactose on the skeleton provided.
Explain how the inclusion of carbohydrates in plastics makes them biodegradable.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«reaction in which» two reactants/molecules/functional groups bond/react «to form a larger molecule/single main product»
small/tiny molecule
OR
H2O formed
Accept formula or name of a specified small molecule other than water such as ammonia, ethanoic/acetic acid,
ethanol, hydrogen sulfide etc. for M2.
Do not accept just “molecule formed”.
Award [1 max] for an example giving an equation of a condensation reaction such as the formation of a disaccharide.
Accept “alpha” or “beta” form of galactose.
Any two of:
makes the plastic more hydrophilic/water soluble
carbohydrates are broken down/hydrolysed by bacteria/microorganisms
makes plastic more accessible to bacteria as holes/channels are created
OR
plastic of lower density is more permeable/susceptible to water/oxygen/heat/pressure
weakens intermolecular/London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces «between polymer chains in the plastic»
Accept “van der Waals/vdW” for “London” forces.
[Max 2 Marks]
Question
Saturated lipids found in butter and unsaturated lipids found in fish oil readily become rancid.
Identify the type of rancidity occurring in saturated lipids and the structural feature that causes it.
State one factor that increases the rate at which saturated lipids become rancid.
Butter contains varying proportions of oleic, myristic, palmitic and stearic acids. Explain in terms of their structures why stearic acid has a higher melting point than oleic acid, using section 34 of the data booklet.
Fish oil is an excellent dietary source of omega-3 fatty acids. Outline one impact on health of consuming omega-3 fatty acids.
Predict the solubility of retinol (vitamin A) in body fat, giving a reason. Use section 35 of the data booklet.
Explain why sharks and swordfish sometimes contain high concentrations of mercury and polychlorinated biphenyls (PCBs).
Plastics are another source of marine pollution. Outline one way in which plastics can be made more biodegradable.
Markscheme
hydrolytic «rancidity»
ester group
Accept a formula for ester group.
[2 marks]
a.i.
«presence of» moisture/water
OR
«increase in» temperature
OR
«presence of» enzymes/bacteria/fungi/mould
OR
low pH/«presence of» acid
Accept “heat”.
[1 mark]
a.ii.
«stearic acid» straight chain/chain has no kinks/more regular structure
OR
«stearic acid» saturated/no «carbon–carbon» double bonds
«stearic acid» chains pack more closely together
stronger London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces «between molecules»
Accept “«stearic acid» greater surface area/electron density”.
[3 marks]
b.
lowers risk of heart disease/atherosclerosis
OR
lowers LDL cholesterol
OR
increases HDL cholesterol
OR
aids brain/neurological development «in children»
OR
relieves rheumatoid arthritis
[1 mark]
c.i.
soluble AND non-polar hydrocarbon chain
Accept as reasons “«predominantly» non-polar” OR “long hydrocarbon chain”.
[1 mark]
c.ii.
not biodegradable
OR
stored/accumulate in fat
biomagnification occurs
OR
concentration increases along food chain
Accept “stored/accumulate in bodies of prey/animals eaten”.
Accept “not excreted”.
[2 marks]
c.iii.
add starch/cellulose/carbohydrates/additives/catalysts «to plastic during manufacture to allow digestion by micro-organisms»
OR
replace traditional plastics with polylactic acid/PLA-based ones
OR
blend traditional and polylactic acid/PLA-based plastics
Accept reference to biodegradable plastics other than PLA; for example polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), poly(butylene succinate) (PBS), polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) and polycaprolactone (PCL).
[1 mark]
c.iv.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
hydrolytic «rancidity»
ester group
Accept a formula for ester group.
[2 marks]
a.i.
«presence of» moisture/water
OR
«increase in» temperature
OR
«presence of» enzymes/bacteria/fungi/mould
OR
low pH/«presence of» acid
Accept “heat”.
[1 mark]
a.ii.
«stearic acid» straight chain/chain has no kinks/more regular structure
OR
«stearic acid» saturated/no «carbon–carbon» double bonds
«stearic acid» chains pack more closely together
stronger London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces «between molecules»
Accept “«stearic acid» greater surface area/electron density”.
[3 marks]
b.
lowers risk of heart disease/atherosclerosis
OR
lowers LDL cholesterol
OR
increases HDL cholesterol
OR
aids brain/neurological development «in children»
OR
relieves rheumatoid arthritis
[1 mark]
c.i.
soluble AND non-polar hydrocarbon chain
Accept as reasons “«predominantly» non-polar” OR “long hydrocarbon chain”.
[1 mark]
c.ii.
not biodegradable
OR
stored/accumulate in fat
biomagnification occurs
OR
concentration increases along food chain
Accept “stored/accumulate in bodies of prey/animals eaten”.
Accept “not excreted”.
[2 marks]
c.iii.
add starch/cellulose/carbohydrates/additives/catalysts «to plastic during manufacture to allow digestion by micro-organisms»
OR
replace traditional plastics with polylactic acid/PLA-based ones
OR
blend traditional and polylactic acid/PLA-based plastics
Accept reference to biodegradable plastics other than PLA; for example polyhydroxyalkanoates (PHA), poly(butylene succinate) (PBS), polybutylene adipate terephthalate (PBAT) and polycaprolactone (PCL).
[1 mark]
c.iv.
Question
Green Chemistry reduces the production of hazardous materials and chemical waste.
Outline two specific examples or technological processes of how Green Chemistry has accomplished this environmental impact.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Any two of:
replaces plastics with biodegradable/starch/cellulose based plastics
use enzymes instead of polluting detergents/phosphates
OR
use of enzymes means lower temperatures can be used
OR
use enzymes instead of emulsifiers to treat oil spills
OR
use enzymes to produce esters at lower temperatures/without sulfuric acid
replace organic/toxic solvents with carbon dioxide
replace polymers from fossil fuel with bamboo/renewable resources
develop paint resins reducing production of volatile compounds «when paint is applied»
industrial synthesis of ethanoic/acetic acid from methanol and carbon monoxide has 100% atom economy
energy recovery
Accept formulas for names.
Award mark for any other reasonable specific green chemistry example that prevents the release of pollutants/toxic chemicals into the environment by changing the method or the materials used.
Do not award mark for methods that involve clean-up of pollutants from the environment such as host-guest chemistry or alternative energy sources.
[2 marks]
Examiners report
[N/A]
