Question
\text { Gasoline (petrol), biodiesel and ethanol are fuels. }
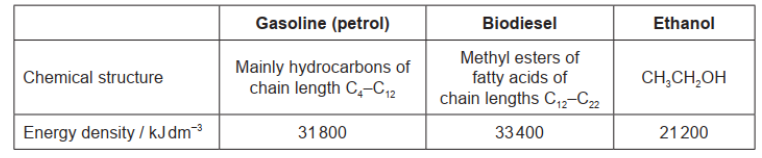
a. Calculate the energy released, in $\mathrm{kJ}$, from the complete combustion of $5.00 \mathrm{dm}^3$ of ethanol.
b. State a class of organic compounds found in gasoline.
c. Outline the advantages and disadvantages of using biodiesel instead of gasoline as fuel for a car. Exclude any discussion of cost.

d. A mixture of gasoline and ethanol is often used as a fuel. Suggest an advantage of such a mixture over the use of pure gasoline. Exclude any discussion of cost.
e(i)When combusted, all three fuels can release carbon dioxide, a greenhouse gas, as well as particulates. Contrast how carbon dioxide and particulates interact with sunlight.
e(ii) Methane is another greenhouse gas. Contrast the reasons why methane and carbon dioxide are considered significant greenhouse gases.
e(iiisuggest a wavenumber absorbed by methane gas.
e(inDetermine the relative rate of effusion of methane $\left(M_{\mathrm{r}}=16.05\right)$ to carbon dioxide $\left(M_{\mathrm{r}}=44.01\right)$, under the same conditions of temperature and pressure. Use section 1 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. $« 21200 \mathrm{~kJ} \mathrm{dm}^{-3} \times 5.00 \mathrm{dm}^3=» 106000 / 1.06 \times 10^5\langle\mathrm{~kJ} 》\rangle$
b. alkane
$O R$
cycloalkane
OR
arene
Accept “alkene”.
Do not accept just “hydrocarbon”, since given in stem.
Do not accept “benzene/aromatic” for “arene”.
c. Advantages: [2 max]
renewable
uses up waste «such as used cooking oil»
lower carbon footprint/carbon neutral
higher flashpoint
produces less $\mathrm{SO}_{\mathrm{x}} / \mathrm{SO}_2$
OR
less polluting emissions
has lubricating properties
OR
preserves/increases lifespan of engine
increases the life of the catalytic converter
eliminates dependence on foreign suppliers
does not require pipelines/infrastructure «to produce»
relatively less destruction of habitat compared to obtaining petrochemicals
Accept “higher energy density” OR “biodegradable” for advantage.
Disadvantages: [2 max]
needs conversion/transesterification
takes time to produce/grow plants
takes up land
OR
deforestation
fertilizers/pesticides/phosphates/nitrates «used in production of crops» have negative environmental effects
biodiversity affected
OR
loss of habitats «due to energy crop plantations»
cannot be used at low temperatures
variable quality «in production»
high viscosity/can clog/damage engines
Accept “lower specific energy” as disadvantage.
Do not accept “lower octane number” as disadvantage”.
d. Any one:
uses up fossil fuels more slowly
lower carbon footprint/CO2 emissions
undergoes more complete combustion
produces fewer particulates
higher octane number/rating
OR
less knocking
prevents fuel injection system build up
OR
helps keep engine clean
Accept an example of a suitable advantage even if repeated from 11c.
e(i)carbon dioxide allows sunlight/short wavelength radiation to pass through AND particulates reflect/scatter/absorb sunlight
Accept “particulates reflect/scatter/absorb sunlight AND carbon dioxide does not”.
Accept ” $\mathrm{CO}_2$ absorbs IR “radiation” AND particulates reflect/scatter/absorb sunlight”.
Do not accept “traps” for “absorbs”.
e(iicarbon dioxide is highly/more abundant «in the atmosphere»
methane is more effective/potent «as a greenhouse gas» OR
methane/better/more effective at absorbing IR «radiation» OR
methane has greater greenhouse factor OR methane has greater global warming potential/GWP
Accept “carbon dioxide contributes more to global warming” for M1.
$\mathrm{e}$ (iiiąny value or range within $\left.2850-3090 \ll \mathrm{cm}^{-1}\right)$
$\mathrm{e}\left(\mathrm{iv}\right.$ ) rate of effusion of $\frac{\mathrm{CH}_4}{\mathrm{CO}_2}=\sqrt{\frac{44.01}{16.05}}=» 1.656$
Question
E10 is composed of $10 \%$ ethanol and $90 \%$ normal unleaded fuel.
a. Ethanol has a Research Octane Number (RON) of 108.6.
Outline how higher octane fuels affect engine performance.
b. Show that, for combustion of equal masses of fuel, ethanol $\left(M_r=46 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\right)$ has a lower carbon footprint than octane $\left(M_r=114 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}\right)$.
c. Biodiesel containing ethanol can be made from renewable resources.
Suggest one environmental disadvantage of producing biodiesel from renewable resources.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. increased $A N D$ fuels can be compressed more «before ignition» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Note: Accept “engines can be designed with higher compression ratio” OR “less chance of pre-ignition/autoignition/ knocking occurring”.
b. Alternative 1
$$
\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH}(\mathrm{I})+3 \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}
$$
(I) / 1 mol ethanol produces $2 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{CO}_2$
OR
$$
\mathrm{C}_8 \mathrm{H} 18(\mathrm{I})+12.5 \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 8 \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+9 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l}) / 1 \mathrm{~mol} \text { octane produces } 8 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{CO} \mathrm{CO}_2[\boldsymbol{V}]
$$
For $1 \mathrm{~g}$ of fuel:
« $\frac{1 \mathrm{~g}}{46 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}} \times 2 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})=» 0.04$ «mol CO $2(\mathrm{~g}) »$ from ethanol $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
« $\frac{1 \mathrm{~g}}{114 \mathrm{~g} \mathrm{~mol}^{-1}} \times 8 \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})=» 0.07 « \mathrm{~mol} \mathrm{CO} \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g}) »$ from octane $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Alternative 2
ratio of $\mathrm{C}$ in ethanol:octane is $2: 8$, so ratio in carbon dioxide produced per mole will be $1: 4$ [ $]$ ratio amount of fuel in $1 \mathrm{~g}=\frac{1}{46}: \frac{1}{114}=2.5: 1$ [ $]$
$4>2.5$ so octane produces more carbon dioxide
OR
ratio of amount of carbon dioxide $=2.5: 4=1: 1.61$ so octane produces more «for combustion of same mass» [ $\checkmark$ ]
c. use of «farm» land «for production»
OR
deforestation «for crop production for fuel»
OR
can release more $\mathrm{NO}_{\mathrm{x}}$ «than normal fuel on combustion» $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
Note: Ignore any reference to cost.
Question
This question is about biofuel.
a. The structure of chlorophyll is given in section 35 of the data booklet.
State the feature of the chlorophyll molecule that enables it to absorb light in the visible spectrum.
b. Evaluate the use of biodiesel in place of diesel from crude oil.
Strength:
Limitation:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. large/extensive «electronic» conjugation
OR
«contains» many alternate single and double bonds
OR
extended system of alternating double and single bonds [ ]
Note: Student response must indicate a large or extended system to award mark.
b. Strength
Any one of:
less flammable «than diesel» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
recycles carbon «lower carbon footprint»
OR
lower greenhouse gas emissions $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
easily biodegradable «in case of spill» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
renewable
OR
does not deplete fossil fuel reserves $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
economic security/availability in countries without crude oil $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
Limitation
Any one of:
more difficult to ignite inside the engine «than diesel» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
more viscous «than diesel» $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
lower energy content/specific energy/energy density $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
uses food sources
$O R$
uses land that could be used for food $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
«production is» more expensive $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
less suitable in low temperatures $[\boldsymbol{V}]$
increased $\mathrm{NO}_{\mathrm{x}}$ emissions for biodiesel $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
greenhouse gases still produced $[\boldsymbol{\sim}]$
Note: Accept “”close to» carbon neutral”, “produce less greenhouse gases/ $\mathrm{CO}_2$ “.
Accept “engines have to be modified if biodiesel used” as limitation.
Do not award marks for strength and limitation that are the same topic/concept.
Question
Ethanol is a biofuel that can be mixed with gasoline.
a. Write the equation for the complete combustion of ethanol.
b. Outline the evidence that relates global warming to increasing concentrations of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere.
c. Explain, including a suitable equation, why biofuels are considered to be carbon neutral.
d. State the type of reaction that occurs when ethanol reacts with vegetable oil to form biodiesel.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. $\mathrm{C}_2 \mathrm{H}_5 \mathrm{OH}(\mathrm{I})+3 \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g}) \rightarrow 2 \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+3 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{I})$
,b. Any two of:
«showing strong» correlation between «atmospheric» $\mathrm{CO}_2$ concentration/greenhouse gas concentration and average “global/surface/ocean» temperature
lab evidence that greenhouse gases $/ \mathrm{CO}_2$ absorb(s) infrared radiation «advanced» computer modelling
ice core data
tree ring data
ocean sediments / coral reefs / sedimentary rocks data
NOTE: Do not accept “global warming” for “average temperature”.
Do not accept “traps/reflects heat” OR “thermal energy”.
Evidence must be outlined and connected to data.
Accept references to other valid greenhouse gases other than carbon dioxide/ $\mathrm{CO}_2$, such as methane $/ \mathrm{CH}_4$ or nitrous oxide/ $/ \mathrm{N}_2 \mathrm{O}$.
c. biofuel raw material/sugar/glucose formed by photosynthesis
OR
biofuel raw material/sugar/glucose uses up carbon dioxide during its formation
OR
biofuel from capturing gases due to decaying organic matter formed from photosynthesis
$6 \mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})+6 \mathrm{H}_2 \mathrm{O}(\mathrm{l}) \rightarrow \mathrm{C}_6 \mathrm{H}_{12} \mathrm{O}_6(\mathrm{aq})+6 \mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g})$
NOTE: Accept arguments based on material coming from plant sources consuming carbon dioxide/carbon for M1.
d. transesterification
OR «nucleophilic» substitution/ $\mathrm{S}_N$
Question
Solar energy, which is freely available, is indispensable to life on earth.
a. Suggest another advantage and one disadvantage of solar energy.

b. Light can be absorbed by chlorophyll and other pigments. Consider molecules $\mathbf{A}$ and $\mathbf{B}$ represented below.
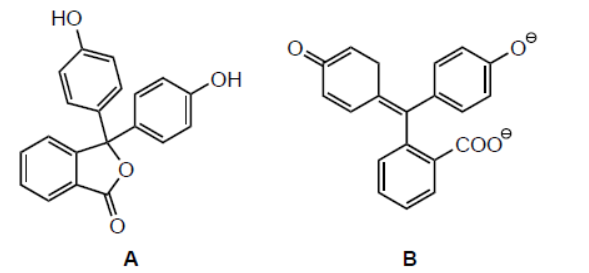
Identify, with a reason, the molecule that absorbs visible light.
c.i. State a physical property of vegetable oils that makes them very difficult to use as fuel in internal combustion engines.
c.ii.Describe how vegetable oils can be converted to a more suitable fuel.
d. Contrast the importance of carbon dioxide and methane as greenhouse gases.
e. Explain, using an equation, the effect of increased carbon dioxide in the atmosphere on the pH of lake water.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. Advantage:
renewable «energy source»
OR
does not produce greenhouse gases
OR
can be installed «almost» anywhere
OR
low maintenance costs
Disadvantage:
widely dispersed/not concentrated «form of energy»
OR
geography/weather/seasonal dependent
OR
not available at night
OR
energy storage is difficult/expensive
OR
toxic/hazardous materials used in production
OR
concerns about space/aesthetics/local environment where installed
$O R$
need to be «constantly» cleaned
Accept “can be used for passive/active heating”, “can be converted to electric energy”.
Accept any specific greenhouse gas name or formula for “greenhouse gases”.
Accept “solar cells require large areas”, “solar cell manufacture produces pollution/greenhouse gases”, “higher cost of solar cells “compared with traditional sources such as fossil fuels or hydroelectric»”.
b. B AND larger/more extensive «electronic» conjugation
OR
B $A N D$ «contains» more alternate single and double bonds
Accept more specific statements, such as “sp ${ }^3$ carbon in A prevents conjugation between aromatic rings”.
c.i. high viscosity
Accept “low volatility”, just “viscous/viscosity” OR “does not flow easily”.
c.ii.convert to esters of monoatomic alcohols
OR
react with short-chain alcohols «in the presence of acid or base»
Accept “convert to shorter «carbon chain» esters” OR “transesterification”.
Accept specific alcohols, such as methanol or ethanol.
d. carbon dioxide/ $\mathrm{CO}_2$ more/most abundant « $\mathrm{GHG}$ than methane/ $\mathrm{CH}_4$ “
OR
carbon dioxide/ $\mathrm{CO}_2$ has «much» longer atmospheric life «than methane/ $\mathrm{CH}_4$ »
methane/ $\mathrm{CH}_4$ «much» better/more effective at absorbing IR radiation «than carbon dioxide/ $/ \mathrm{CO}_2$ “
OR
methane/ $\mathrm{CH}_4$ has a greater greenhouse factor «than carbon dioxide/ $\mathrm{CO}_2$ »
OR
methane/ $/ \mathrm{CH}_4$ has a greater global warming potential/GWP «than carbon dioxide/ $\mathrm{CO}_2$ »
. f cr
Question
Vegetable oils and diesel fuel have similar energy content but vegetable oils are not usually used as fuels in internal combustion engines.
Transesterification reactions allow waste cooking oils to be converted to biofuels. Identify a reagent and catalyst required for this conversion.
Reagent:
Catalyst:
Deduce the equation for the reaction that occurs assuming that the vegetable oil has the formula drawn below.
Scientists around the world conduct research into alternatives to fossil fuels. Suggest why collaboration is important.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
Reagent:
methanol/CH3OH
OR
ethanol/C2H5OH
Do not accept just “alcohol”.
Catalyst:
strong acid
OR
strong base
Accept any strong acid such as sulfuric acid/ H2SO4 .
Accept any strong base such as sodium hydroxide/NaOH.
correct structure of ester product
formula of glycerol AND balanced equation
Do not penalize omission of equilibrium sign.
Accept use of ethanol/other alcohol as reactant with the corresponding products.
Accept full or condensed structural formulas of products.
different solutions/statistical data can be compared/combined
OR
best ideas can be shared to arrive at global/local solutions
OR
acceleration of research
OR
discoveries become available to everyone
OR
improved confidence in validity of results «if multiple scientists/research groups are involved»
OR
money/effort/time is not wasted duplicating work others have already done
Do not accept scientists simply working together to share ideas – look for a little more detail.
Accept other valid suggestions.
Question
Biofuels are renewable energy sources derived mainly from plants.
State the equation for the complete transesterification of the triglyceride given below with methanol.
Outline why the fuel produced by the reaction in (a) is more suitable for use in diesel engines than vegetable oils.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
methyl ester formula AND glycerol formula
correct balancing
Award M2 only if M1 is correct.
«methyl esters have» low«er» viscosity/surface tensions
OR
«methyl esters have» high«er» volatility
OR
«combustion of vegetable oils» produces carbon deposits in engine/reduces engine life
Accept converse arguments.
Question
Vegetable oils, such as that shown, require conversion to biodiesel for use in current internal combustion engines.
State two reagents required to convert vegetable oil to biodiesel.
Deduce the formula of the biodiesel formed when the vegetable oil shown is reacted with the reagents in (a).
Explain, in terms of the molecular structure, the critical difference in properties that makes biodiesel a more suitable liquid fuel than vegetable oil.
Determine the specific energy, in kJ\(\,\)g−1, and energy density, in kJ\(\,\)cm−3, of a particular biodiesel using the following data and section 1 of the data booklet.
Density = 0.850 g\(\,\)cm−3; Molar mass = 299 g\(\,\)mol−1;
Enthalpy of combustion = 12.0 MJ\(\,\)mol−1.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
methanol
OR
ethanol
strong acid
OR
strong base
Accept “alcohol”.
Accept any specific strong acid or strong base other than HNO3/nitric acid.
[3 marks]
CH3(CH2)16COOCH3 / CH3OCO(CH2)16CH3
OR
CH3(CH2)16COOC2H5 / C2H5OCO(CH2)16CH3
Product must correspond to alcohol chosen in (a), but award mark for either structure if neither given for (a).
[1 mark]
lower viscosity
weaker intermolecular/dispersion/London/van der Waals’ forces
OR
smaller/shorter molecules
Accept “lower molecular mass/Mr” or “lower number of electrons”.
Accept converse arguments.
[2 marks]
Specific energy: «\( = \frac{{12\,000{\text{ kJ}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ – 1}}}}{{299{\text{ g}}\,{\text{mo}}{{\text{l}}^{ – 1}}}}\)» = 40.1 «kJ g−1»
Energy density: «= 40.1 kJ\(\,\)g−1 x 0.850 g\(\,\)cm−3» = 34.1 «kJ\(\,\)cm−3»
Award [1] if both are in terms of a unit other than kJ (such as J or MJ).
[2 marks]
Question
The sun is the main source of energy used on earth.
One fusion reaction occurring in the sun is the fusion of deuterium, \({}_1^2H\), with tritium, \({}_1^3H\), to form helium, \({}_2^4He\). State a nuclear equation for this reaction.
Explain why this fusion reaction releases energy by using section 36 of the data booklet.
State the technique used to show that the sun is mainly composed of hydrogen and helium.
Coloured molecules absorb sunlight. Identify the bonding characteristics of such molecules.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({}_1^2H\) + \({}_1^3H\) → \({}_2^4He\) + \({}_0^1n\)
Accept “n” for “\({}_0^1n\)”
Accept “2H + 3H → 4He + 1n/n”.
[1 mark]
higher binding energy/BE «per nucleon» for helium/products
OR
nucleons in products more tightly bound
mass defect/lost matter converted to energy
Accept converse statement in M1.
Accept “mass deficit” for “mass defect”.
[2 marks]
spectrometry
Accept “spectroscopy” for “spectrometry” OR more specific techniques such as “atomic absorption spectrometry/AAS”, “astrophotometry” etc. Do not award mark for incorrect specific spectrometric techniques.
Do not accept “spectrum”.
[1 mark]
«extensive system of» conjugation/alternating single and double «carbon to carbon» bonds
OR
delocalized electrons «over much of the molecule»
[1 mark]
Question
Vegetable oils can be used as a source of energy.
State the structural feature of chlorophyll that enables it to absorb visible light.
Vegetable oils are too viscous for use as liquid fuels. Describe, using an equation, how a vegetable oil, such as that shown, is converted to oils with lower viscosity by reaction with methanol, CH3OH.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
«extensive» conjugation
OR
alternating single and double bonds
ester product
glycerol AND correct balancing
Catalyst not required for equation.
Award M2 only if M1 is correct.
Question
One suggestion for the reduction of carbon footprints is the use of biofuels, such as vegetable oils, as a substitute for petroleum based fuels.
Outline the major technical problem affecting the direct use of vegetable oils as fuels in internal combustion engines and the chemical conversion that has overcome this.
State the formula of a fuel that might be produced from the vegetable oil whose formula is shown.
Outline why biofuels are considered more environmentally friendly, even though they produce more carbon dioxide per kJ of energy than petroleum based fuels.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
viscosity «of vegetable oils is too high»
transesterification
OR
«conversion into» alkyl/methyl/ethyl esters
[2 marks]
R–CO–O–CH3/RCOOMe
OR
R–CO–O–C2H5/RCOOEt
[1 mark]
«growing oil producing» plants absorbs carbon dioxide from the atmosphere
OR
«combustion of» petroleum based fuels releases carbon stored «for millions of years»
Accept “biofuels renewable” OR “petroleum based fuels non-renewable”.
Accept “waste vegetable oils can be converted to biofuels/biodiesel”.
Accept “biofuels do not contain sulfur”.
[1 mark]
Question
One method of producing biodiesel is by a transesterification process.
Deduce the equation for the transesterification reaction of pentyl octanoate, C7H15COOC5H11, with methanol.
Outline why the ester product of this reaction is a better diesel fuel than pentyl octanoate.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
C7H15COOC5H11(l) + CH3OH(l) → C7H15COOCH3(l) + C5H11OH(l)
OR
C13H26O2(l) + CH4O(l) → C9H18O2(l) + C5H12O(l)
OR
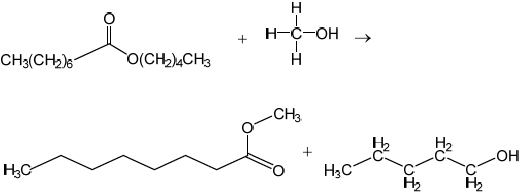
Accept correct equation in any format eg, skeletal, condensed structural formula, etc.
Accept equations with equilibrium arrow.
[1 mark]
less viscous «and so does not need to be heated to flow»
OR
less likely to undergo incomplete combustion
OR
fewer intermolecular/London/dispersion forces
OR
vaporizes easier
Ignore equation and products in 14a.
Accept “van der Waals’/vdW” for “London”.
[1 mark]

