Question
(a) Photosynthesis enables green plants to store energy from sunlight as glucose.
(i) Write the equation for photosynthesis.
(ii) Identify the structural feature that allows chlorophyll to absorb light. Use section 35 of the data booklet.
(iii) Explain how photosynthesis is being employed to control global warming.
(b) Photovoltaic cells also convert sunlight into energy.
(i) State the form of energy produced by photosynthesis and photovoltaic cells.
Photosynthesis:
Photovoltaic:
(ii) Explain how a silicon-based photovoltaic cell brings about this conversion.
(c) Glucose can be converted to ethanol through fermentation:
\(C_6H_{12}O_6 (aq) → 2C_2H_5OH(aq) + 2CO_2 (g)\)
(i) Determine the energy efficiency of this conversion in terms of the enthalpies of combustion of the reactants and products. Use section 13 of the data booklet.
(ii) Suggest one reason, other than energy density and specific energy, why ethanol may be considered a more useful fuel than glucose.
(d) Both ethanol and glucose can be used to generate energy through fuel cells.
(i) Outline one way fuel cells differ from primary cells.
(ii) State one way to increase the maximum current of a voltaic cell.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) (i) \(6CO_2(g) + 6H_2O(l) → C_6H_{12}O_6(aq) + 6O_2(g)\)
(ii) conjugated «electronic» structure/delocalized «pi» electrons/alternate «single and» double bonds
(iii) reduces/sequesters \(CO_2\)/carbon dioxide «concentration from atmosphere»
«planting» more plants/trees
(b) (i) Photosynthesis: chemical
AND
Photovoltaic: electrical
(ii) Any three of:
n-type AND p-type «silicon layers»
OR
n-type doped with Gp 15 element/P AND p-type doped with Gp 13 element/B
potential difference/charge separation created between layers of silicon
«sunlight produces» free electrons that flow between layers «from p-type to n-
type»
OR
«sunlight produces» positive holes that flow between layers «from n-type to p-
type»
«excess» electrons move “from n-type to p-type” through an external circuit
(c) (i) «(2x-1367 / -2803) x 100 =» 97.54%
OR
2.46% loss «in energy efficiency»
(ii) liquid
OR
easier ignition
OR
more volatile
(d) (i) material provides energy in fuel cells
OR
fuel continually added in fuel cells
(ii) reduce «internal» resistance
Question
Biofuels can be synthesized or converted to make them more usable.
(a) Write the equation for the fermentation of glucose, \(C_6H_{12}O_6\), to produce ethanol.
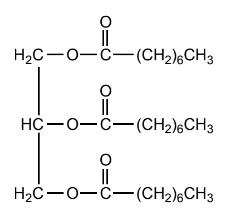
(b) Deduce the equation for the reaction of the triglyceride shown with methanol.
(c) Outline the essential feature needed for a molecule to convert light energy into chemical energy.
(d) The Geobacter bacterium anaerobically oxidizes substances present in the substrate of microbial fuel cells. For example, ethanoate ions, \(CH_3COO^-\)(aq), are oxidized to carbon dioxide gas.
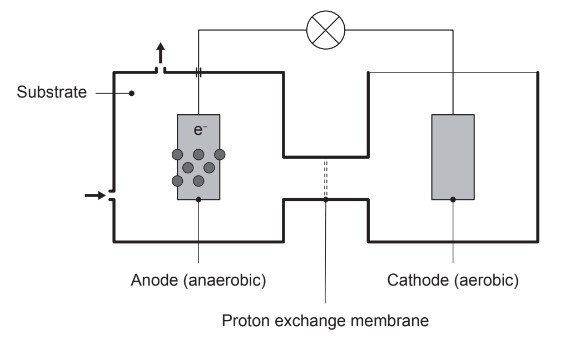
(i) Outline the function of the proton exchange membrane.
(ii) Write equations for the reactions occurring at the anode and cathode, and an overall equation for a microbial fuel cell containing ethanoate ions.
Anode:
Cathode:
Overall equation:
(iii) Suggest one reason why microbial fuel cells might be a sustainable energy source.
Answer/Explanation
Answer:
(a) \(C_6H_{12}O_6 \rightarrow 2C_2H_5OH + 2CO_2\)
(b) 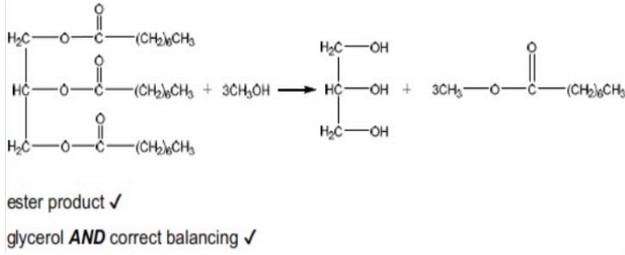
(c) conjugated bonds/alternating C=C bonds/delocalized electrons/bonding
(d) (i) allow \(H^+\) ions to pass through/diffuse/move «from anode to cathode»
(ii) Anode: \(CH_3COO^-(aq) + 2H_2O(l) \rightarrow 2CO_2(g) + 7H+(aq) + 8e^-\)
Cathode: \(O_2(g) + 4H^+(aq) + 4e^- \rightarrow 2H_2O(l)\)
Overall Equation: \(CH_3COO^-(aq) + H^+(aq) + 2O_2(g) \rightarrow 2CO_2(g) + 2H_2O(l)\)
(iii) fuel supply is wastewater/organic material
