Question
State the condensed electron configurations for: [2]
i. Cr:
ii. Cr3+:
▶️Answer/Explanation
Ans:
Cr: [Ar] 4s13d5
Cr3+: [Ar] 3d3
Accept “[Ar] 3d54s1 ”.
Accept “[Ar] 3d34s0 ”. A
ward [1 max] for two correct full electron configurations “1s22s22p63s23p64s13d5 AND 1s22s22p63s23p63d3 ”. Award [1 max] for 4s13d5 AND 3d3
Detailed Solution:
i. The electronic configuration of chromium (Cr) is “1s22s22p63s23p63d54s1 or [Ar] 3d54s1
[Ar]: Represents the electron configuration of the noble gas argon (atomic number 18).
ii. The electronic configuration of chromium (Cr3+) is “1s22s22p63s23p63d3 or [Ar] 3d3
[Ar]: Represents the electron configuration of the noble gas argon (atomic number 18).
Question
a.The relative atomic mass of naturally occurring copper is 63.55. Calculate the abundances of \(^{{\text{63}}}{\text{Cu}}\) and \(^{{\text{65}}}{\text{Cu}}\) in naturally occurring copper[2]
b.The isotopes of some elements are radioactive. State a radioisotope used in medicine.[1]
c.State a balanced equation for the reaction of sodium with water. Include state symbols.[2]
(i) potassium iodide.
(ii) potassium fluoride.[3]
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. \(63x + 65(1 – x) = 63.55\);
(or some other mathematical expression).
\(^{63}{\text{Cu}} = 72.5\% \) and \(^{65}{\text{Cu}} = 27.5\% \);
Allow 63Cu = 0.725 and 65Cu = 0.275.
Award [2] for correct final answer.
60Co /131I /125I;
Must contain correct mass numbers.
Allow other formats such as cobalt-60, Co-60 etc.
Award no marks if a correct radioisotope is given with an incorrect radioisotope.
Allow any other radioisotope if you can verify its use.
\({\text{2Na(s)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \to {\text{2NaOH(aq)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g) / Na(s)}} + {{\text{H}}_2}{\text{O(l)}} \to {\text{NaOH(aq)}} + \frac{1}{2}{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}}\)
Award [1] for correct balanced equation.
Award [1] for correct state symbols for sodium, water, sodium hydroxide and hydrogen.
Second mark is not dependent on equation being correctly balanced.
(Rb more reactive because) electron lost further from nucleus so less tightly held;
Rb electron is in 5th energy level and (Na less reactive) as electron lost in 3rd energy level / OWTTE;
Allow [1 max] for electron arrangements of Na (e.g. 2,8,1) and Rb if second mark is not scored.
(i) solution becomes yellow/orange/brown/darker;
chlorine is more reactive than iodine (and displaces it from solution) / OWTTE;
Allow correct equation (KI + Cl2 \( \to \) KCl + I2) for second mark or stating that iodine/I2 is formed.
(ii) no colour change/nothing happens as fluorine is more reactive than chlorine / OWTTE;
Detailed Explanation:
a. Relative atomic mass = Sum of products of isotope mass and fraction abundance
Let fraction abundance of Cu-63 be x.
63.55 = 63x + 65(1-x)
x=0.725
Cu-63 = 72.5% and Cu-65 = 27.5%.
b. Radioisotopes are widely used in medicine for various diagnostic and therapeutic purposes. Some commonly used radioisotopes in medicine include:Iodine-131, Cobalt-60,Gallium-67 etc.
c.
The balanced equation for the reaction of sodium (Na) with water (H2O) is as follows:
2Na + 2H2O -> 2NaOH + H2
In this reaction, sodium reacts with water to produce sodium hydroxide (NaOH) and hydrogen gas (H2). The equation is balanced, as there are equal numbers of atoms of each element on both sides of the equation.
d. The reaction between rubidium (Rb) and water is more vigorous than that between sodium (Na) and water due to the larger size and lower ionization energy of rubidium compared to sodium. Rubidium is located below sodium in Group 1 of the periodic table. As you move down the group, the size of the atoms increases due to the addition of more electron shells. Rubidium atoms are larger than sodium atoms, which means they have more electron-electron repulsion and a more loosely held outer electron.
e.
i.
When chlorine gas (Cl2) is bubbled through a solution of potassium iodide (KI), a redox reaction occurs. The chlorine gas oxidizes iodide ions (I-) to iodine (I2) while being reduced itself. The balanced chemical equation for this reaction is as follows:
Cl2 + 2KI -> 2KCl + I2
In this reaction, the chlorine gas reacts with potassium iodide to form potassium chloride (KCl) and elemental iodine (I2). The chlorine gas is reduced from a zero oxidation state to a -1 oxidation state in potassium chloride, while iodide ions are oxidized from a -1 oxidation state to a zero oxidation state in iodine. The liberated iodine can be observed as a characteristic brown color, indicating the formation of I2. The potassium ions (K+) remain in solution as spectator ions and do not participate in the redox reaction.
ii. if chlorine gas is bubbled through a solution of potassium fluoride, no colour change/nothing happens as fluorine is more reactive than chlorine.
Question
Draw and label an energy level diagram for the hydrogen atom. In your diagram show how the series of lines in the i. Ultraviolet and
ii. Visible regions of its emission spectrum are produced, clearly labelling each series.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
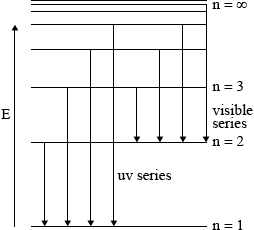
showing y-axis labelled as energy/E / labelling at least two energy levels;
showing a minimum of four energy levels/lines with convergence;
showing jumps to n = 1 for ultraviolet series;
showing jumps to n = 2 for visible light series;
Must show at least two vertical lines per series to score M3 and M4 but penalize once only.
For M3, M4 if transition not shown from higher to lower energy level penalize only once.
Detailed Solution:

i. Lyman Series (Ultraviolet): The Lyman series corresponds to electron transitions to the n = 1 energy level. When an electron drops from higher energy levels to the n = 1 level, it emits photons in the ultraviolet region. The spectral lines in the Lyman series are not visible to the naked eye. The first line in the Lyman series (n = 2 to n = 1 transition) corresponds to the Lyman-alpha line at 121.6 nm.
ii. Balmer Series (Visible): The Balmer series corresponds to electron transitions to the n = 2 energy level. When an electron drops from higher energy levels to the n = 2 level, it emits photons in the visible region of the electromagnetic spectrum. The Balmer series includes several visible spectral lines. The first line in the Balmer series (n = 3 to n = 2 transition) corresponds to the H-alpha line at 656.3 nm, which appears as red light.
