Question
Metals are extracted from their ores by various means.
Aluminium is produced by the electrolysis of alumina (aluminium oxide) dissolved in cryolite.
a. Discuss why different methods of reduction are needed to extract metals.
b(ii)Write half-equations for the electrolysis of molten alumina using graphite electrodes, deducing the state symbols of the products.
Anode (positive electrode):
Cathode (negative electrode):
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. ions of more reactive metals are harder to reduce
OR
more reactive metals have more negative electrode potentials
electrolysis is needed/used for most reactive metals
OR
carbon is used to reduce metal oxides of intermediate reactivity/less reactive than carbon
OR
heating ore is sufficient for less reactive metals
NOTE: Award [1 max] for “«ease of reduction/extraction» depends on reactivity”.
$b(i)$ electronegativity difference $=1.8$ «and average electronegativity $=2.5$ »
$57 \ll \% »$
NOTE: Accept any value in the range 52-65\%.
Award [2] for correct final answer.
b(ii)Anode (positive electrode):
$$
2 \mathrm{O}^{2-} \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{e}^{-}+\mathrm{O}_2(\mathrm{~g})
$$
OR
$$
2 \mathrm{O}^{2-}+\mathrm{C} \rightarrow 4 \mathrm{e}^{-}+\mathrm{CO}_2(\mathrm{~g})
$$
NOTE: Award [1 max] for M1 and M2 if correct half-equations are given at the wrong electrodes OR if incorrect reversed half-equations are given at the correct electrodes.
Cathode (negative electrode):
$$
\mathrm{Al}^{3+}+3 \mathrm{e}^{-} \rightarrow \mathrm{Al}(\mathrm{I}) \sim
$$
$\mathrm{O}_2$ gas $\boldsymbol{A N D}$ Al liquid
NOTE: Only state symbols of products required, which might be written as (g) and (I) in half-equations. Ignore any incorrect or missing state symbols for reactants.
Question
Lanthanum, La, and antimony, $\mathrm{Sb}$, form compounds with bromine that have similar formulas, $\mathrm{LaBr}_3$ and $\mathrm{SbBr}_3$.
a. Determine the type of bond present in $\mathrm{SbBr}_3$, showing your method. Use sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
b. Lanthanum has a similar electronegativity to group 2 metals. Explain, in terms of bonding and structure, why crystalline lanthanum bromide is brittle.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. polar covalent
average electronegativity $«=\frac{1}{2}(3.0+2.0) »=2.5$ AND electronegativity difference $«=3.0-2.0 »=1.0$
[2 marks]
b. ionic bonding
OR
electrostatic forces between ions
«slight» movement brings ions of same charge adjacent to each other «causing the crystal to break»
OR
“slight» movement results in repulsion between layers «causing the crystal to break»
Question
Polymers are made up of repeating monomer units which can be manipulated in various ways to give structures with desired properties.
a. (i) Draw the structure of 2-methylpropene.
(ii) Deduce the repeating unit of poly(2-methylpropene).
b. Deduce the percentage atom economy for polymerization of 2-methylpropene.
c. (i) Suggest why incomplete combustion of plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride, is common in industrial and house fires.
(ii) Phthalate plasticizers such as DEHP, shown below, are frequently used in polyvinyl chloride.
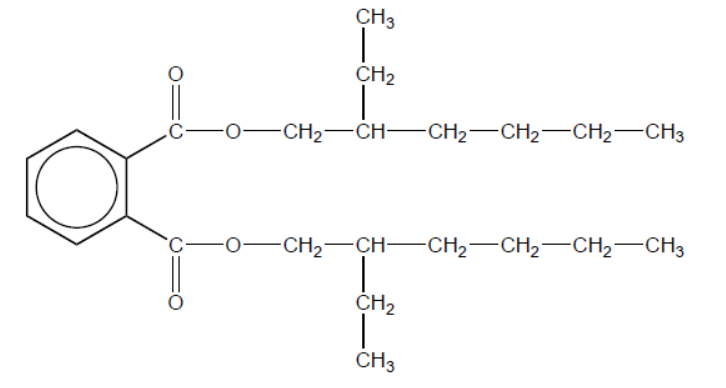
With reference to bonding, suggest a reason why many adults have measurable levels of phthalates in their bodies.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. i.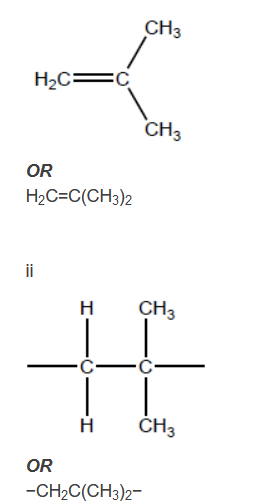
Continuation bonds needed for mark.
No penalty if square brackets present or ” $n$ ” appears after the bracket/formula.
b. «same mass of product as reactant, thus» $100 \ll \% »$
Accept “less than 100\%” only if a reason is given (eg, the catalyst is not converted into the product, or other reasonable answer).
C. i
due to stability of plastics/strong covalent bonds
OR
low volatility preventing good mixing with oxygen «gas»
OR
lack of/insufficient oxygen
OR
plastics are often parts of devices with non-combustible components «which mechanically prevent the combustion of plastic components»
OR
PVC already partly oxidised «because some $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{H}$ bonds are replaced with $\mathrm{C}-\mathrm{Cl}$ bonds», so it cannot produce enough heat for complete combustion
OR
many industrial/household materials contain additives that reduce their flammability/act as flame retardants
ii
weakly bound to the PVC/no covalent bonds to PVC/only London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces between DEHP and PVC AND leach/evaporate «from PVC» to atmosphere/food chain
OR
has low polarity/contains non-polar hydrocarbon chains $A N D$ fat-soluble/deposits in the fatty tissues
OR
has unusual structural fragments/is a xenobiotic/difficult to metabolise AND stays in the body for a long time
Question
Materials science involves understanding the properties of materials and applying those properties to desired structures.
a. Magnesium oxide, MgO, and silicon carbide, $\mathrm{SiC}$, are examples of ceramic materials. State the name of the predominant type of bonding in each material.
b. Predict the predominant type of bonding for a binary compound AB in which the electronegativity of both atoms is low. Use section 29 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
a. MgO: ionic AND SiC: covalent
Accept “covalent network/network covalent” for “covalent” but not just “network”.
b. metallic «bonding»
Question
Materials science involves understanding the properties of materials and applying those properties to desired structures.
Magnesium oxide, MgO, and silicon carbide, SiC, are examples of ceramic materials. State the name of the predominant type of bonding in each material.
Predict the predominant type of bonding for a binary compound AB in which the electronegativity of both atoms is low. Use section 29 of the data booklet.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
MgO: ionic AND SiC: covalent
Accept “covalent network/network covalent” for “covalent” but not just “network”.
metallic «bonding»
Question
Polymers are made up of repeating monomer units which can be manipulated in various ways to give structures with desired properties.
(i) Draw the structure of 2-methylpropene.
(ii) Deduce the repeating unit of poly(2-methylpropene).
Deduce the percentage atom economy for polymerization of 2-methylpropene.
(i) Suggest why incomplete combustion of plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride, is common in industrial and house fires.
(ii) Phthalate plasticizers such as DEHP, shown below, are frequently used in polyvinyl chloride.
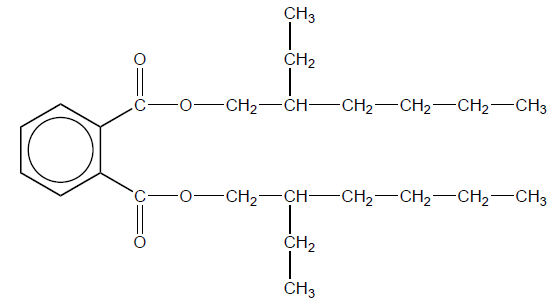
With reference to bonding, suggest a reason why many adults have measurable levels of phthalates in their bodies.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
i
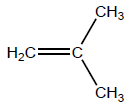
OR
H2C=C(CH3)2
ii
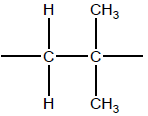
OR
−CH2C(CH3)2−
Continuation bonds needed for mark.
No penalty if square brackets present or “n” appears after the bracket/formula.
«same mass of product as reactant, thus» 100«%»
Accept “less than 100%” only if a reason is given (eg, the catalyst is not converted into the product, or other reasonable answer).
i
due to stability of plastics/strong covalent bonds
OR
low volatility preventing good mixing with oxygen «gas»
OR
lack of/insufficient oxygen
OR
plastics are often parts of devices with non-combustible components «which mechanically prevent the combustion of plastic components»
OR
PVC already partly oxidised «because some C–H bonds are replaced with C–Cl bonds», so it cannot produce enough heat for complete combustion
OR
many industrial/household materials contain additives that reduce their flammability/act as flame retardants
ii
weakly bound to the PVC/no covalent bonds to PVC/only London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces between DEHP and PVC AND leach/evaporate «from PVC» to atmosphere/food chain
OR
has low polarity/contains non-polar hydrocarbon chains AND fat-soluble/deposits in the fatty tissues
OR
has unusual structural fragments/is a xenobiotic/difficult to metabolise AND stays in the body for a long time
Question
Lanthanum, La, and antimony, Sb, form compounds with bromine that have similar formulas, LaBr3 and SbBr3.
Determine the type of bond present in SbBr3, showing your method. Use sections 8 and 29 of the data booklet.
Lanthanum has a similar electronegativity to group 2 metals. Explain, in terms of bonding and structure, why crystalline lanthanum bromide is brittle.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
polar covalent
average electronegativity «= \(\frac{1}{2}\)(3.0 + 2.0)» = 2.5 AND electronegativity difference «= 3.0 – 2.0» = 1.0
[2 marks]
ionic bonding
OR
electrostatic forces between ions
«slight» movement brings ions of same charge adjacent to each other «causing the crystal to break»
OR
«slight» movement results in repulsion between layers «causing the crystal to break»
[2 marks]

