Question
Ethylamine, \({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\), is a weak base.
State the equation for the reaction of ethylamine with water.
Explain why ethylamine has basic properties.
State the formula and deduce the shape of the positive ion (cation) formed when triethylamine, \({{\text{(}}{{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{)}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{N}}\), reacts with hydrochloric acid.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\({{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}} + {{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{O}} \rightleftharpoons {{\text{C}}_{\text{2}}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{5}}}{\text{NH}}_{\text{3}}^ + + {\text{O}}{{\text{H}}^ – }\);
Accept \( \to \) in place of \( \rightleftharpoons \).
non-bonding/lone pair of electrons on the N atom (enables proton/\({{\text{H}}^ + }\) acceptance) / OWTTE;
\({{\text{(}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}{\text{)}}_3}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}^ + }/{{\text{[(}}{{\text{C}}_2}{{\text{H}}_5}{{\text{)}}_3}{\text{NH]}}^ + }\);
tetrahedral;
Examiners report
Majority of the candidates scored the mark for part (a). Lack of reference to N and lone pairs in part (b) penalized many candidates in scoring the mark. Most candidates were unable to explain the stronger basic properties diethylamine in part (c). Responses indicated weak understanding of the inductive effect of the alkyl groups. Many candidates did not address it the increased inductive effect due to two alkyl groups.
Majority of the candidates scored the mark for part (a). Lack of reference to N and lone pairs in part (b) penalized many candidates in scoring the mark. Most candidates were unable to explain the stronger basic properties diethylamine in part (c). Responses indicated weak understanding of the inductive effect of the alkyl groups. Many candidates did not address it the increased inductive effect due to two alkyl groups.
Majority of the candidates scored the mark for part (a). Lack of reference to N and lone pairs in part (b) penalized many candidates in scoring the mark. Most candidates were unable to explain the stronger basic properties diethylamine in part (c). Responses indicated weak understanding of the inductive effect of the alkyl groups. Many candidates did not address it the increased inductive effect due to two alkyl groups.
Question
Polymers are made up of repeating monomer units which can be manipulated in various ways to give structures with desired properties.
(i) Draw the structure of 2-methylpropene.
(ii) Deduce the repeating unit of poly(2-methylpropene).
Deduce the percentage atom economy for polymerization of 2-methylpropene.
(i) Suggest why incomplete combustion of plastic, such as polyvinyl chloride, is common in industrial and house fires.
(ii) Phthalate plasticizers such as DEHP, shown below, are frequently used in polyvinyl chloride.
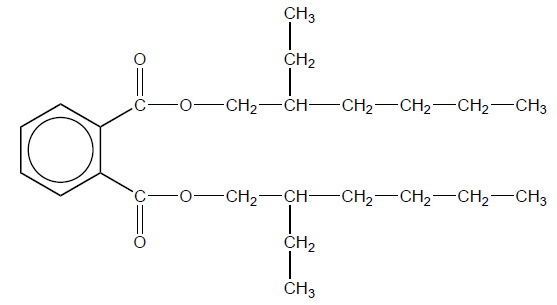
With reference to bonding, suggest a reason why many adults have measurable levels of phthalates in their bodies.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
i
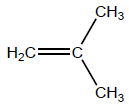
OR
H2C=C(CH3)2
ii
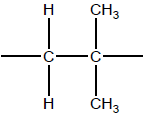
OR
−CH2C(CH3)2−
Continuation bonds needed for mark.
No penalty if square brackets present or “n” appears after the bracket/formula.
«same mass of product as reactant, thus» 100«%»
Accept “less than 100%” only if a reason is given (eg, the catalyst is not converted into the product, or other reasonable answer).
i
due to stability of plastics/strong covalent bonds
OR
low volatility preventing good mixing with oxygen «gas»
OR
lack of/insufficient oxygen
OR
plastics are often parts of devices with non-combustible components «which mechanically prevent the combustion of plastic components»
OR
PVC already partly oxidised «because some C–H bonds are replaced with C–Cl bonds», so it cannot produce enough heat for complete combustion
OR
many industrial/household materials contain additives that reduce their flammability/act as flame retardants
ii
weakly bound to the PVC/no covalent bonds to PVC/only London/dispersion/instantaneous induced dipole-induced dipole forces between DEHP and PVC AND leach/evaporate «from PVC» to atmosphere/food chain
OR
has low polarity/contains non-polar hydrocarbon chains AND fat-soluble/deposits in the fatty tissues
OR
has unusual structural fragments/is a xenobiotic/difficult to metabolise AND stays in the body for a long time
Question
The table summarizes some properties of graphite and graphene.
Graphene is two-dimensional, rather than three-dimensional, material.
Justify this by using the structure of graphene and information from the table.
Show that graphene is over 1600 times stronger than graphite.
Identify a value from the table which can be used to support the information about graphene given below.
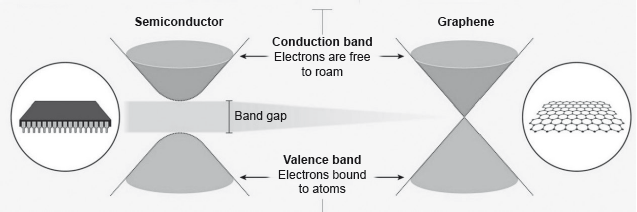
Electrons in a solid are restricted to certain ranges, or bands, of energy (vertical axis). In an insulator or semiconductor, an electron bound to an atom can break free only if it gets enough energy from heat or a passing photon to jump the “band gap”, but in graphene the gap is infinitely small. 
Diamond, graphene, and graphite are all network solids.
Suggest, giving a reason, the electron mobility of diamond compared to graphene.
The melting point of diamond at 1 × 106 kPa is 4200 K (in the absence of oxygen).
Suggest, based on molecular structure, why graphene has a higher melting point under these conditions.
▶️Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
consists of single/one sheet/layer «of carbon atoms»
graphene has no density measurement
OR
graphene has no distance between layers data
OR
graphene has large specific surface area «compared to graphite»
Do not accept “sp2” alone without reference to single/one sheet/layer.
Accept “thickness of one atom” OR “consists of a plane” for M1.
[2 marks]
Any one of these alternatives:
ALTERNATIVE 1
«\(\frac{{1.3 \times {{10}^{11}}}}{{76 \times {{10}^6}}}\)»
1.7 × 103/1711
ALTERNATIVE 2
1600 × 76 × 106 = 1.2 × 1011 «is less than tensile strength of graphene»
ALTERNATIVE 3
\(\frac{{1.3 \times {{10}^{11}}}}{{1600}}\) = 8.1 × 107 «is greater than upper end of tensile strength for graphite»
Accept any value in the range 1700–27 083. Answer may be expressed in scientific notation or otherwise.
Accept any value calculated which is less than the graphene tensile strength based on a value chosen from within the 4.8–76 × 106 range.
[1 mark]
«graphene has a high electron mobility of» 15 000–200 000 «cm2 V–1 s–1»
A specific value or range of values must be given.
Accept any value in the 15 000–200 000 «cm2 V–1 s–1» range.
[1 mark]
smaller/zero
no delocalized electrons/electrons are bound/electrons not free to move/electrons not free to roam
OR
localized electrons «in sigma bonds»
OR
large band gap
Accept “diamond is a dielectric” OR “diamond does not conduct electricity” for M2.
Award [1 max] for just “immobile/less mobile”.
Award [2] for “electrons immobile «in diamond» due to the large band gap” OR “electrons «in diamond» immobile
since electrons are localized «in the sigma bonds»”.
[2 marks]
shorter bonds in graphene
OR
bonds in graphene intermediate between single and double
OR
bond order in graphene is 1.33
OR
delocalization creates stronger bonds
OR
shorter bonds are stronger
stronger/shorter bonds require higher temperature/faster thermal motion to be altered
OR
stronger/shorter bonds require greater energy to be broken
[2 marks]

