Question
(a)(i) Sketch the titration curve of methanoic acid with sodium hydroxide, showing how you would determine methanoic acid pKa. [2]
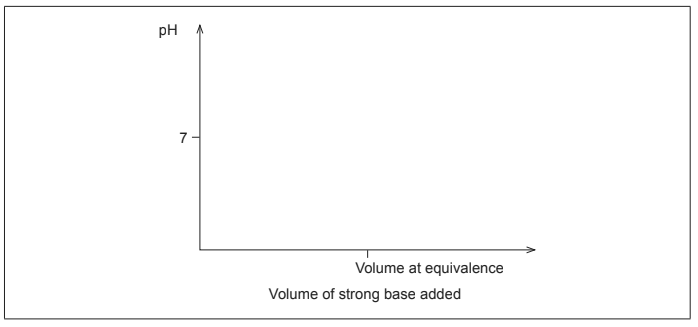
(ii) Identify an indicator that could be used for the titration in 5(d)(i), using section 22 of the data booklet. [1]
(b) Determine the concentration of methanoic acid in a solution of pH = 4.12. Use section 21 of the data booklet. [2]
(c) Identify if aqueous solutions of the following salts are acidic, basic, or neutral. [2]
Sodium methanoate:
Ammonium chloride:
Sodium nitrate:
Answer/Explanation
Ans
a i
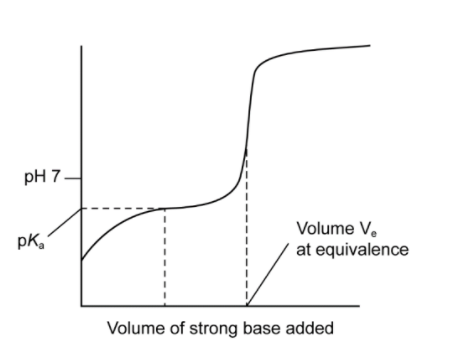
increasing S-shape pH curve
pKa: pH at half neutralization/equivalence
M1: Titration curve must show buffer region at pH <7 and equivalence at pH >7. Ignore other parts of the curve, i.e., before buffer region, etc.
Accept curve starting from where two axes meet as pH scale is not specified.
a ii phenolphthalein OR phenol red
b
Alternative 1: Ka = OR [HCOOH] =
«[HCOOH] =» 3.24 × 10−5 «mol dm−3»
Alternative 2: «pH = pKa + log 4.12 = 3.75 + log
«[HCOOH] =» 3.24 × 10−5 «mol dm−3»
Award [2] for correct final answer.
c
Sodium methanoate:
basic Ammonium chloride:
acidic Sodium nitrate: neutral
Question
A student decided to determine the molecular mass of a solid monoprotic acid, HA, by titrating a solution of a known mass of the acid.
The following recordings were made.
![]()
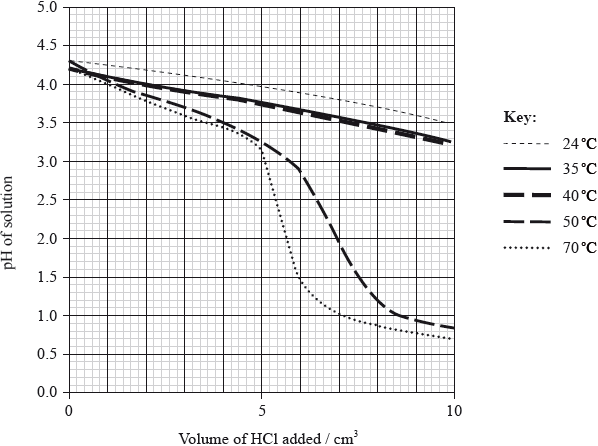
To investigate the effect of temperature on the effectiveness of a buffer solution, the student placed \({\text{20.0 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of the buffer solution in a water bath at 24 °C. He added small portions of hydrochloric acid, stirring after each addition, until a total of \({\text{10 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) was added, and measured the pH continuously during the addition. The procedure was repeated at different temperatures and the results are shown in the following graph.
Determine the molecular formula of HA.[2]
State what is meant by a buffer solution.[2]
With reference to the graph on page 4, describe the effect of increasing temperature on the effectiveness of the buffer solution.[2]
Answer/Explanation
Markscheme
\(\left( {\frac{{\text{M}}}{{{\text{Mass of }}{{\text{C}}_4}{{\text{H}}_4}{\text{O}}}} = } \right){\text{ }}\frac{{139}}{{68.08}} = 2\);
\({{\text{C}}_8}{{\text{H}}_8}{{\text{O}}_2}\);
Award [2] for correct final answer.
solution which resists change in pH / changes pH slightly / keeps pH constant / OWTTE;
when small amounts of acid or base are added;
less effective at higher temperatures / more effective between 24 °C and 40 °C than > 40 °C;
pH changes more if the same volume of acid is added at high(er) temperature / OWTTE;
Examiners report
Errors were carried forward in the marking of (d).
The common error in defining a buffer solution in (f) (i) was to omit “small” in the addition of acid or alkali whilst in (ii) candidates needed to be more specific about the volume of acid added for full credit.
