Question
Ultraviolet radiation has a shorter wavelength than infrared radiation. How does the frequency and energy of ultraviolet radiation compare with infrared radiation?
▶️Answer/Explanation
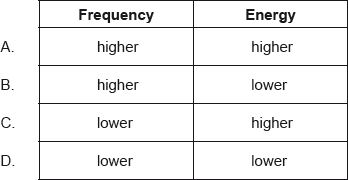
A
E=hf=hc/λ
Energy and frequency are inversely proportional to the wavelength.
Ultraviolet radiation has a shorter wavelength than infrared radiation. Its frequency and energy will be higher than infrared radiation.
Question
Which feature of a molecule can be determined from its 1H NMR spectrum?
A. Number of hydrogen environments
B. Total mass of hydrogen atoms present
C. Vibration frequency of C–H bonds
D. Ionization energy of a hydrogen atom
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
If the 1H NMR spectrum is available for an unknown compound, counting the number of signals in the spectrum tells us the number of different sets of protons in the molecule, and that is the very important information to determine the structure of the compound. Therefore, we can determine the number of different hydrogen environments in the molecule.
Question
Which molecule has an index of hydrogen deficiency (IHD) = 1?
A. C6H6
B. C2Cl2
C. C4H9N
D. C2H6O
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD), is a count of how many molecules of H2 need to be added to a structure in order to obtain the corresponding saturated, acyclic species.
If you have a molecular formula, CcHhNnOoXx, then the following equation: IHD = 0.5 * [2c+2-h-x+n]
For C6H6 , IHD = 0.5*[2*6+2-6] = 4.
For C2Cl2, Each Cl atom is treated as H for calculating IHD i.e. C2H2 IHD = 0.5*[2*2+2-2] = 2.
C4H9N, IHD = 0.5*[2*4+2-9+1] = 1.
C2H6O, IHD = 0.5*[2*2+2-6] = 0.
Question
What is the Index of Hydrogen Deficiency (IHD) for 1,3,5-hexatriene (C6H8)?
A. 1
B. 3
C. 5
D. 6
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
If you have a molecular formula, CcHhNnOoXx,
IHD = 0.5 * [2c+2-h-x+n]
Here, c=6, h=8
IHD = 0.5 * [2*6+2-8] = 3.
Question
Which information can be gained from an infrared (IR) spectrum?
A. Ionization energy of the most abundant element
B. Number of different elements in the compound
C. Bonds present in a molecule
D. Molecular formula of the compound
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Infrared Spectroscopy is the analysis of infrared light interacting with a molecule. This can be analyzed in three ways by measuring absorption, emission and reflection. The main use of this technique is in organic and inorganic chemistry. It is used by chemists to determine functional groups in molecules. IR Spectroscopy measures the vibrations of atoms, and based on this it is possible to determine the functional groups.5 Generally, stronger bonds and light atoms will vibrate at a high stretching frequency (wavenumber).
Thus, an infrared (IR) spectrum can be used to determine the functional groups in molecules which can tell us about the bonds present in that molecule.
Question
What can be deduced from the following 1H\(\,\)NMR spectrum?
A. There is only one hydrogen atom in the molecule.
B. There is only one hydrogen environment in the molecule.
C. The molecule is a hydrocarbon.
D. There is only one isotope in the element.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The position of a signal along the x-axis of an NMR spectra is called chemical shift, or δ, of the signal. Chemical shift is determined by the structural electronical environment of the nuclei producing that signal. Protons in different chemical environments (non-equivalent) show signals at different chemical shift.
Since there is only one chemical shift in the given NMR spectrum, it means there is only one hydrogen environment in the molecule.
Question
What information is provided by 1H NMR, MS and IR for an organic compound?
I. 1H NMR: chemical environment(s) of protons
II. MS: fragmentation pattern
III. IR: types of functional group
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
If the 1H NMR spectrum is available for an unknown compound, counting the number of signals in the spectrum tells us the number of different sets of protons in the molecule, and that is the very important information to determine the structure of the compound. Thus, the 1H NMR spectrum tells about the chemical environment(s) of protons.
Inorganic Mass Spectrometry(MS) is specifically used to determine the elemental and isotopic composition of the material being analyzed. The techniques are capable of the measurement of a range of concentrations from major components to ultra trace constituents. Thus, MS gives the fragmentation pattern.
Infrared Spectroscopy is the analysis of infrared light interacting with a molecule. This can be analyzed in three ways by measuring absorption, emission and reflection. The main use of this technique is in organic and inorganic chemistry. It is used by chemists to determine functional groups in molecules. IR Spectroscopy measures the vibrations of atoms, and based on this it is possible to determine the functional groups.5 Generally, stronger bonds and light atoms will vibrate at a high stretching frequency (wavenumber). Thus, IR is used to determine functional groups in molecules.
