Question
The activation energy of a reaction may be determined by studying the effect of a particular variable on the reaction rate. Which variable must be changed?
A. pH
B. Concentration
C. Surface area
D. Temperature
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
k = Ae-Ea/RT
ln k = ln(Ae-Ea/RT)
ln k = ln(A) + (-Ea/RT) = ln(A) – (Ea/R)(1/T)
The activation energy can also be calculated directly given two known temperatures and a rate constant at each temperature. Using above equation , suppose that at two different temperatures T1 and T2, reaction rate constants k1 and k2:
ln k1 = ln(A) – Ea/RT1
ln k2 = ln(A) – Ea/RT2
ln(k1) – ln(k2) = Ea/RT2 – Ea/RT1
ln(k1/k2)=Ea/RT2 – Ea/RT1
Thus, temperature must be changed to determine Ea value.
Question
What happens when the temperature of a reaction increases?
A. The activation energy increases.
B. The rate constant increases.
C. The enthalpy change increases.
D. The order of the reaction increases.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
As per Arrhenius law,
k = Ae-Ea/RT
With increase in temperature, the rate constant increases.
Question
The rate constant for a reaction is determined at different temperatures. Which diagram represents the relationship between the rate constant, \(k\) , and temperature, \(T\) , in K ?
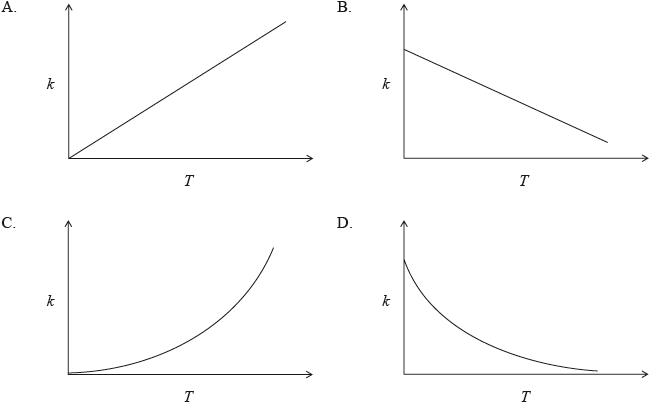
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
k = Ae-Ea/RT
It is an exponential graph with k tending towards 0 at T=0.
Question
What happens to the rate constant, k, and the activation energy, \({E_{\text{a}}}\), as the temperature of a chemical reaction is increased?
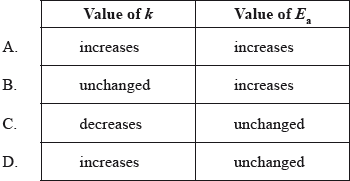
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
k = Ae-Ea/RT
k increases as temperature increases.
Activation energy is independent of temperature.
Question
Which of the terms in the Arrhenius equation takes into account the orientation of the molecules?
\[k = A{e^{\frac{{ – {E_a}}}{{RT}}}}\]
B. Ea
C. R
D. T
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
\[k = A{e^{\frac{{ – {E_a}}}{{RT}}}}\]
Here, A is frequency factor constant or also known as pre-exponential factor or Arrhenius factor. It indicates the rate of collision and the fraction of collisions with the proper orientation for the reaction to occur.
Question
Which is true of an Arrhenius plot of \(\ln k\) (y-axis) against \(\frac{1}{T}\)?
A. The graph goes through the origin.
B. The activation energy can be determined from the gradient.
C. The intercept on the x-axis is the activation energy.
D. The intercept on the y-axis is the frequency factor, A.
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
As per Arrhenius equation,
k = Ae-Ea/RT
ln k = ln(Ae-Ea/RT)
ln k = ln(A) + (-Ea/RT) = ln(A) – (Ea/R)(1/T)
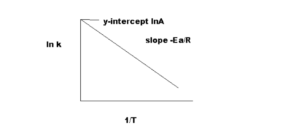
Intercept on y axis is lnA.
Slope is -Ea/R. R is the gas constant. Hence, Ea can be determined from slope.
