Question
Which mixtures could act as buffers?
I. NaOH(aq) and HCl(aq)
II. NaOH(aq) and \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COOH(aq)}}\)
III. HCl(aq) and \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COONa(aq)}}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The buffer solution is either solution of weak acid and its salt with strong base or solution of weak base and its salt with strong acid.
In I, the given combination, HCl and NaOH, are strong acid and strong base, respectively. When mixed in an aqueous solution, they get ionized completely. Hence, the combination of HCl and NaOH does not make a buffer solution.
In II, NaOH is strong base and acetic acid is weak acid.
In III, HCl is strong acid and \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{COONa(aq)}}\) is salt of a weak acid.
Hence, II and III will form buffer solution.
Question
Which indicator would be the most appropriate for titrating aqueous ethylamine, \({\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{C}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}\), with nitric acid, \({\text{HN}}{{\text{O}}_{\text{3}}}\)?
A. Bromophenol blue \({\text{(p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = {\text{ }}4{\text{.}}1)\)
B. Bromothymol blue \({\text{(p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = {\text{ }}7{\text{.}}3)\)
C. Phenol red \({\text{(p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = {\text{ }}8{\text{.}}0)\)
D. Thymolphthalein \({\text{(p}}{K_{\text{a}}} = {\text{ }}10{\text{.}}0)\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Here, a weak base ethylamine and strong nitric acid are being titrated. For the titration of a weak base, where the pH at the equivalence point is less than 7.0, an indicator such as methyl red or bromocresol blue or bromophenol blue, with pKin < 7.0, should be used.
Question
Question
Equal volumes and concentrations of hydrochloric acid and ethanoic acid are titrated with sodium hydroxide solutions of the same concentration. Which statement is correct?
A. The initial pH values of both acids are equal.
B. At the equivalence points, the solutions of both titrations have pH values of 7.
C. The same volume of sodium hydroxide is needed to reach the equivalence point.
D. The pH values of both acids increase equally until the equivalence points are reached.
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The number of moles of acid = number of moles of base for complete neutralization at equivalence point.
Hence, the volume of base ( sodium hydroxide ) of particular concentration required would be exactly same in case of equal volumes and concentrations solutions of both strong acid (HCl) and weak acid (ethanoic acid) to reach the equivalence point.
Question
Bromophenol blue changes from yellow to blue over the pH range of 3.0 to 4.6. Which statement is correct?
A. Molecules of bromophenol blue, HIn, are blue.
B. At \({\text{pH}} < 3.0\), a solution of bromophenol blue contains more ions, \({\text{I}}{{\text{n}}^ – }\), than molecules, HIn.
C. The \({\text{p}}{K_{\text{a}}}\) of bromophenol blue is between 3.0 and 4.6.
D. Bromophenol blue is a suitable indicator to titrate ethanoic acid with potassium hydroxide
solution.
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
Indicators change colour when pH value is around their pKa values. Since bromophenol blue changes from yellow to blue over the pH range of 3.0 to 4.6. Hence, The pKa of bromophenol blue is between 3.0 and 4.6.
At pH<3, HIn does not dissociate much. It remains predominantly in HIn form.
In D, it is the titration of a weak acid with a strong base, the conjugate base of the weak acid will make the pH at the equivalence point greater than 7. Therefore, you would want an indicator to change in that pH range. So, Bromophenol blue is not suitable here.
Question
Which compounds can be mixed together as solutions of equal volume and concentration to form a buffer solution?
A. Nitric acid and potassium hydroxide
B. Nitric acid and potassium nitrate
C. Propanoic acid and potassium hydroxide
D. Propanoic acid and potassium propanoate
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
The buffer solution is either solution of weak acid and its salt with strong base or solution of weak base and its salt with strong acid.
In D, it is a solution of weak propanoic acid and its salt potassium propanoate.
Potassium hydroxide is a strong base and nitric acid is a strong acid. Hence their solutions do not form buffer solutions.
Question
The graph below shows the titration curve of \({\text{25 c}}{{\text{m}}^{\text{3}}}\) of \({\text{0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ – 3}}\) of hydrochloric acid with sodium hydroxide, of \({\text{0.100 mol}}\,{\text{d}}{{\text{m}}^{ – 3}}\) concentration. The indicator methyl orange was used to determine the equivalence point. Methyl orange has a pH range of 3.2– 4.4.
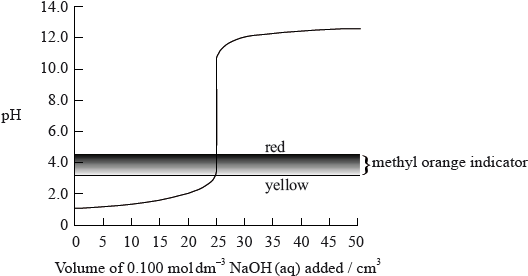
If the hydrochloric acid was replaced by ethanoic acid of the same volume and concentration, which property of the titration would remain the same?
A. The initial pH
B. The pH at the equivalence point
C. The volume of strong base, NaOH, needed to reach the equivalence point
D. The colour of the titration mixture just before the equivalence point is reached
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The number of moles of acid = number of moles of base for complete neutralization at equivalence point.
So, when a weak acid (ethanoic acid) is used instead of strong hydrochloric acid, then the volume of weak acid (ethanoic acid) required would be same as that of strong acid (HCl) at same concentration, to neutralize the NaOH base.
