Question
Between which ionization energies of boron will there be the greatest difference?
A. Between 1st and 2nd ionization energies
B. Between 2nd and 3rd ionization energies
C. Between 3rd and 4th ionization energies
D. Between 4th and 5th ionization energies
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
B: 1s2.2s2.2p1
Upto 3rd ionization energies, electrons are removed from 2p and 2s orbitals.
But during 4th ionization energy, electron is removed from stable noble gas configuration of Helium.
4th ionization energy will be much much higher than 3rd ionization energy. Hence the greatest difference will be between 3rd and 4th ionization energies.
Question
The graph below shows the first four ionization energies of four elements A, B, C and D (the letters are not their chemical symbols). Which element is magnesium?
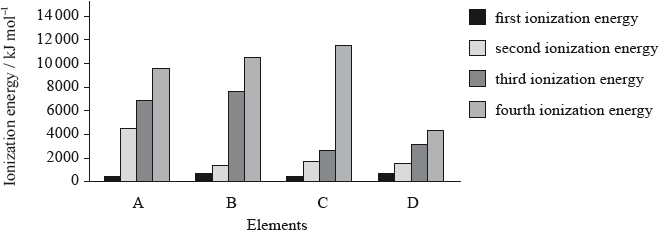
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
As the difference between 2nd and 3rd ionization energies is huge for element B, It is Magnesium. Because during 3rd ionization, electron is to be removed from stable noble gas configuration of Ne.
Question
Values for the successive ionization energies for an unknown element are given in the table below.
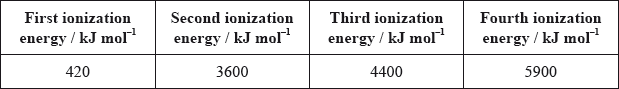
In which group of the periodic table would the unknown element be found?
A. 1
B. 2
C. 3
D. 4
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
As the difference between first and second ionization energies is huge, it attains stable noble gas configuration after first ionization. Hence, it belongs to Group 1.
Question
Which equation represents the second ionization energy of potassium?
A. \({\text{K(g)}} \to {{\text{K}}^{2 + }}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{e}}^ – }\)
B. \({{\text{K}}^ + }{\text{(g)}} \to {{\text{K}}^{2 + }}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{e}}^ – }\)
C. \({\text{K(s)}} \to {{\text{K}}^{2 + }}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{2}}{{\text{e}}^ – }\)
D. \({{\text{K}}^ + }{\text{(s)}} \to {{\text{K}}^{2 + }}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{e}}^ – }\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
During its first ionization, K will loose 1 electron to form K+ cation.
During its second ionization, K+ will loose 1 electron to form K2+ cation.
Question
Successive ionization energies for an element, Z, are shown in the table below.
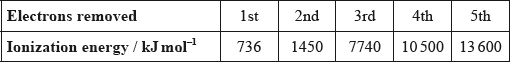
What is the most likely formula for the ion of Z?
A. \({{\text{Z}}^ + }\)
B. \({{\text{Z}}^{2 + }}\)
C. \({{\text{Z}}^{3 + }}\)
D. \({{\text{Z}}^{4 + }}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
There is less difference between 2nd ionization energy after 1st ionization of Z. So, it will undergo 2nd ionization easily.
But there is huge gap between 3rd ionization energy after 2nd ionization of Z. It will not undergo 3rd ionization and will form Z2+ stable cation easily.
