Question
Which process represents the C–Cl bond enthalpy in tetrachloromethane?
A. \({\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{4}}}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{C(g)}} + {\text{4Cl(g)}}\)
B. \({\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_4}({\text{g)}} \to {\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_3}({\text{g)}} + {\text{Cl(g)}}\)
C. \({\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_4}({\text{l)}} \to {\text{C(g)}} + 4{\text{Cl(g)}}\)
D. \({\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_4}({\text{l)}} \to {\text{C(s)}} + 2{\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_2}({\text{g)}}\)
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
The bond enthalpy of a chemical bond can be defined as the total amount of energy required to break 1 mole of that chemical bond.
\({\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_4}({\text{g)}} \to {\text{CC}}{{\text{l}}_3}({\text{g)}} + {\text{Cl(g)}}\)
Here, there are 4 C-Cl bonds in the reactants and 3 C-Cl bonds in the products side. Hence, exactly 1 mole of C-Cl bond is broken in this process, which represents the C–Cl bond enthalpy in tetrachloromethane.
Question
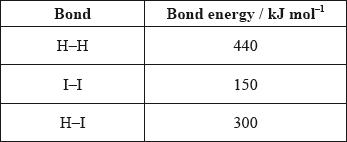
Use the average bond enthalpies below to calculate the enthalpy change, in kJ, for the following reaction.
\[{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2HI(g)}}\]
A. +290
B. +10
C. –10
D. –290
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
\[{{\text{H}}_2}{\text{(g)}} + {{\text{I}}_2}{\text{(g)}} \to {\text{2HI(g)}}\]
ΔHrxn= Energy required to break the bond + Energy released in the formation of a new bond
Here, 1 H-H and 1 I-I bond is broken and 2 H-I bonds are formed.
ΔHrxn = (H-H bond energy + I-I bond energy) – 2(H-I bond energy)
= 440+150-2(300)
= -10 kJ
Question
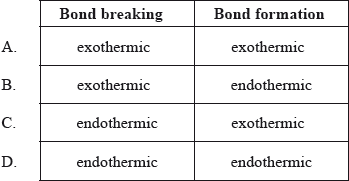
Which combination is correct about the energy changes during bond breaking and bond formation?
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
During the reaction, energy is absorbed to break the bond, which is called the endothermic process and energy is released to form a new bond is called the exothermic process.
Question
Which statement is correct?
A. In an exothermic reaction, the products have more energy than the reactants.
B. In an exothermic reversible reaction, the activation energy of the forward reaction is greater than that of the reverse reaction.
C. In an endothermic reaction, the products are more stable than the reactants.
D. In an endothermic reversible reaction, the activation energy of the forward reaction is greater than that of the reverse reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
If the activation energy of the forward reaction is greater than that of the reverse reaction, the products must have a higher enthalpy than the reactants. The net enthalpy change is therefore positive, meaning that it is endothermic.
In an endothermic reaction, energy is absorbed during the reaction, and the products thus have a larger quantity of energy than the reactants. This means that the products are less stable than the reactants.
Question
Which describes the reaction shown in the potential energy profile?
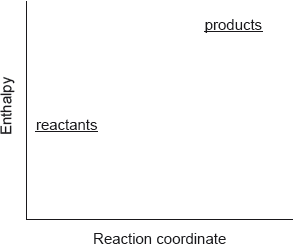
A. The reaction is endothermic and the products have greater enthalpy than the reactants.
B. The reaction is endothermic and the reactants have greater enthalpy than the products.
C. The reaction is exothermic and the products have greater enthalpy than the reactants.
D. The reaction is exothermic and the reactants have greater enthalpy than the products.
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Here, the products have a larger quantity of energy than the reactants, which means energy is absorbed during the reaction. Hence, the reaction is an endothermic reaction and the products have greater enthalpy than the reactants.
