Question
What is the best definition of rate of reaction?
A. The time it takes to use up all the reactants
B. The rate at which all the reactants are used up
C. The time it takes for one of the reactants to be used up
D. The increase in concentration of a product per unit time
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
The reaction rate or rate of reaction is the speed at which a chemical reaction takes place, defined as proportional to the increase in the concentration of a product per unit time and to the decrease in the concentration of a reactant per unit time.
Question
Which factors can affect reaction rate?
I. The state of the reactants
II. The frequency of the collisions between particles
III. The average kinetic energy of the particles
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
According to the collision theory, the rate of reaction increases with the increase in the concentration of the reactants. The more molecules are present, the more collisions will happen. To effectively initiate a reaction, collisions must be sufficiently energetic
(kinetic energy) to bring about this bond disruption.
Question
Equal masses of powdered calcium carbonate were added to separate solutions of hydrochloric acid. The calcium carbonate was in excess. The volume of carbon dioxide produced was measured at regular intervals. Which curves best represent the evolution of carbon dioxide against time for the acid solutions shown in the table below.
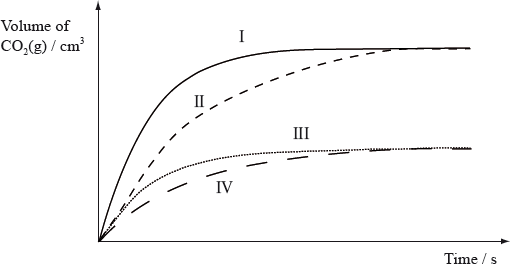
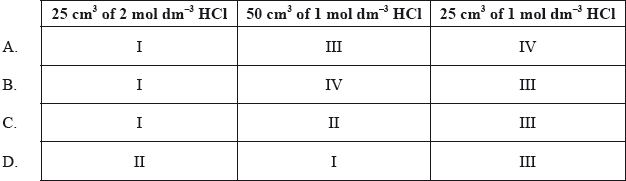
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
CaCO3(s)+2HCl(aq)⟶CaCl2(aq)+H2O(l)+CO2(g)
As calcium carbonate is in excess, it is the concentration and number of moles of HCl that will influence the initial rate of reaction.
Here, Reaction I and II have higher initial rate of reaction as compared to curves III and IV.
Both 25 cm3 of 2 mol dm-3 HCl and 50 cm3 of 1 mol dm-3 HCl have equal 0.05 mol HCl whereas 25 cm3 of 1 mol dm-3 HCl has 0.025 mol HCl.
0.05 mol HCl have higher initial rate of reaction as compared to 0.025 mol HCl.
Now, fastest reaction I will occur in case of 25 cm3 of 2 mol dm-3 HCl as it has smaller volume within which the reaction is taking place which increases the probability of successful collisions.
Reaction II will occur in case of 50 cm3 of 1 mol dm-3 HCl.
Any one of reaction III or IV will occur for 25 cm3 of 1 mol dm-3 HCl.
Hence, correct answer is C.
Question
Consider the reaction between magnesium and hydrochloric acid. Which factors will affect the reaction rate?
I. The collision frequency of the reactant particles
II. The number of reactant particles with \(E \geqslant {E_{\text{a}}}\)
III. The number of reactant particles that collide with the appropriate geometry
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Activation energy can be defined as the minimum amount of energy that is required to activate molecules or atoms so that they can undergo chemical transformation. This minimum energy is to overcome the energy barrier is called activation energy. Reactant particles should have \(E \geqslant {E_{\text{a}}}\) to undergo chemical reaction.
In a chemical reaction, products are formed due to the collision between the reactant molecules. The conditions for the collisions to form products are that collisions should be effective, there should be right orientation of reactant molecules towards each other and all molecules should possess a minimum amount of energy to form product molecules.
Question
Hydrochloric acid is reacted with large pieces of calcium carbonate, the reaction is then repeated using calcium carbonate powder. How does this change affect the activation energy and the collision frequency?
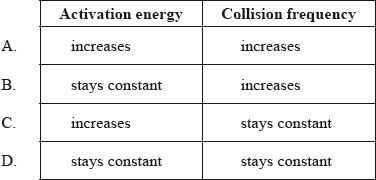
▶️Answer/Explanation
B
Rate of reaction increases as surface area of a solid is increased by breaking the solid into powdered form as there will be greater number of solid particles available for reaction, this will result in greater collision frequency.
But increasing surface area of the reactant will not alter the activation energy of the reaction.
Question
Which graph best represents the relationship between the average kinetic energy of molecules of a gas and temperature in K?
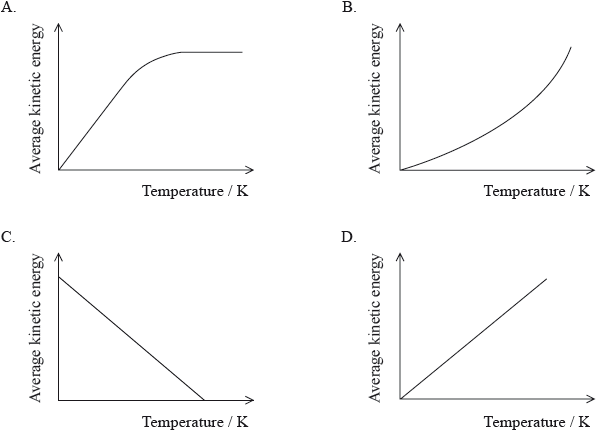
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
Average kinetic energy of gas molecules K=3/2kBT ⟹K∝T
Question
Nitrogen gas reacts with hydrogen gas according to the following equation.
\[{{\text{N}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} + {\text{3}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}} \rightleftharpoons {\text{2N}}{{\text{H}}_{\text{3}}}{\text{(g)}}\;\;\;\;\;\Delta H = – 92{\text{ kJ}}\]
Why is the rate of reaction slow at room temperature?
A. The activation energy of the forward reaction is high.
B. The activation energy of the forward reaction is low.
C. The equilibrium constant is very small.
D. The rate of the reverse reaction is greater than the rate of the forward reaction.
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Before molecules can react, they need to come into close contact with each other, and then have enough energy left to start reacting. At high temperatures this is a lot more likely than at low temperatures, because the average speed of the molecules is higher.
At room temperature, reactants do not have enough energy to cross the high activation energy barrier required to produce ammonia by the given reaction. Hence, rate of the reaction is slow at room temperature.
