Question
What occurs at an anode?
| Voltaic cell | Electrolytic cell |
A | oxidation | reduction |
B | reduction | oxidation |
C | reduction | reduction |
D | oxidation | oxidation |
▶️Answer/Explanation
D
An electrolytic cell can be defined as an electrochemical device that uses electrical energy to facilitate a non-spontaneous redox reaction. Electrolytic cells are electrochemical cells that can be used for the electrolysis of certain compounds. It contain positively charged anode and negatively charged cathode. Reduction occurs at cathode and oxidation occurs at anode.
Galvanic cell or Voltaic cell is an electrochemical cell that makes use of chemical reactions to generate electrical energy.
Anode – Oxidation occurs at this electrode. Cathode – Reduction occurs at this electrode. Salt bridge – Contains electrolytes which are required to complete the circuit in a galvanic cell.
Question
What happens at the negative electrode in a voltaic cell and in an electrolytic cell?
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Anode is negatively charged electrode in a voltaic cell and oxidation occurs at this electrode.
Cathode is negatively charged electrode in an electrolytic cell and reduction occurs at this electrode.
Question
Consider how current is conducted in an electrolytic cell. Which statement is correct?
A. Electrons move through the electrolyte and the external circuit.
B. Ions move through the electrolyte and the external circuit.
C. Electrons move through the external circuit and ions move through the electrolyte.
D. Electrons move through the electrolyte and ions move through the external circuit.
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
In electrolytic cells, electrons move through the external circuit and the electrolyte provides the medium for the exchange of electrons between the cathode and the anode as the ions move through the electrolyte.
Question
Which changes could take place at the positive electrode (cathode) in a voltaic cell?
I. \({\text{Z}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\) to Zn(s)
II. \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\) to \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ – }{\text{(aq)}}\)
III. Mg(s) to \({\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\)
A. I and II only
B. I and III only
C. II and III only
D. I, II and III
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
We know that in a voltaic cell, reduction takes place at the cathode and oxidation takes place at the anode. Here, the correct answer is A, corresponding to I. and II.,
As in I. zinc changes from a +2 oxidation state in \({\text{Z}}{{\text{n}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\) to 0 in Zn(s), which is reduction and
In II. Chlorine changes from a 0 oxidation state in \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}_{\text{2}}}{\text{(g)}}\) to a –1 oxidation state in \({\text{C}}{{\text{l}}^ – }{\text{(aq)}}\).
III. is ruled out as magnesium is in a 0 oxidation state in Mg(s) and changes to a +2 oxidation state in \({\text{M}}{{\text{g}}^{2 + }}{\text{(aq)}}\) which is oxidation.
Question
Metal A is more reactive than metal B. A standard voltaic cell is made as shown.
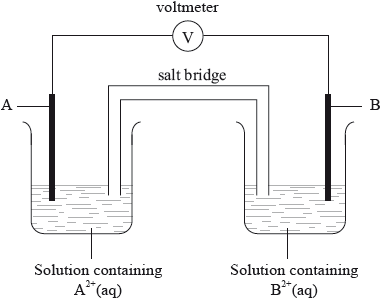
Which statement is correct?
A. Electrons flow in the external circuit from A to B.
B. Positive ions flow through the salt bridge from A to B.
C. Positive ions flow in the external circuit from B to A.
D. Electrons flow through the salt bridge from B to A.
▶️Answer/Explanation
A
Since, A is more reactive than B,
At cathode: B 2+ + 2e– → B
At anode: A → A2+ + 2e–
Since it is a voltaic cell, electrons flow in the external circuit from anode to cathode i.e. from A to B.
Negative ions flow through the salt bridge from B to A.
Question
Which statement is correct for the electrolysis of molten lead iodide, \({\text{Pb}}{{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\)?
A. Chemical energy is converted into electrical energy.
B. \({\text{P}}{{\text{b}}^{2 + }}\) ions are oxidized at the negative electrode (cathode).
C. \({{\text{I}}_{\text{2}}}\) is produced at the positive electrode (anode).
D. Ions are produced at both electrodes.
▶️Answer/Explanation
C
The negative cathode electrode reaction for the electrolysis of molten lead(II) iodide:
The positive lead(II) ions are attracted to the negative electrode and are discharged to form molten lead
Pb2+(l) + 2e– ==> Pb(l).
Positive ion reduction by electron gain. This is a reduction reaction because the lead ions gain electrons.
The positive anode electrode reaction for the electrolysis of molten lead iodide:
The negative bromide ions are attracted to the positive anode electrode and discharged to form iodine I2(g).
2I–(l) ==> I2(g) + 2e– negative ion oxidation by electron loss.
This is an oxidation reaction because the bromide ions lose electrons.
Electrolysis is the process where decomposition of compounds takes place due to electrical energy.
