AP Chemistry Concise Summary Notes - New Syllabus Effective fall 2024
AP Chemistry Concise Summary Notes- New syllabus
Targeted AP Chemistry Concise Summary Notes designed to help you identify your strengths and weaknesses. Focus your study time effectively and maximize your exam performance.
Ace your AP Chemistry exam with these concise summary notes! Quickly review key concepts, formulas, and reactions. Perfect for last-minute studying and boosting your score.
Unit 1: Atomic Structure and Properties
Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and Properties
Unit 3: Intermolecular Forces and Properties
- 3.1 Intermolecular Forces
- 3.2 Properties of Solids
- 3.3 Solids, Liquids, and Gases
- 3.4 Ideal Gas Law
- 3.5 Kinetic Molecular Theory
- 3.6 Deviation from Ideal Gas Law
- 3.7 Solutions and Mixtures
- 3.8 Representations of Solutions
- 3.9 Separation of Solutions and Mixtures Chromatography
- 3.10 Solubility
- 3.11 Spectroscopy and the Electromagnetic Spectrum
- 3.12 Properties of Photons
- 3.13 Beer-Lambert Law
Unit 4: Chemical Reactions
Unit 5: Kinematics
- 5.1 Reaction Rate
- 5.2 Introduction to Rate Law
- 5.3 Concentration Change Over Time
- 5.4 Elementary Reactions
- 5.5 Collision Model
- 5.6 Reaction Energy Profile
- 5.7 Introduction to Reaction Mechanisms
- 5.8 Reaction Mechanism and Rate Law
- 5.9 Steady State Approximation
- 5.10 Multisteps Reaction Energy profile
- 5.11 Catalyst
Unit 7: Equilibrium
- 7.1 Introduction to Equilibrium
- 7.2 Direction of Reversible Reactions
- 7.3 Reaction Quotient and Equilibrium Constant
- 7.4 Calculating the Equilibrium Constant
- 7.5 Magnitude of the Equilibrium Constant
- 7.6 Properties of the Equilibrium Constant
- 7.7 Calculating Equilibrium Concentrations
- 7.8 Representations of Equilibrium
- 7.9 Introduction to Le Châtelier’s Principle
- 7.10 Reaction Quotient and Le Châtelier’s Principle
- 7.11 Introduction to Solubility Equilibria
- 7.12 Common-Ion Effect
Unit 8: Acids and Bases
- 8.1 Introduction to Acids and Bases
- 8.2 pH and pOH of Strong Acids and Bases
- 8.3 Weak Acid and Base Equilibria
- 8.4 Acid-Base Reactions and Buffers
- 8.5 Acid-Base Titrations
- 8.6 Molecular Structure of Acids and Bases
- 8.7 pH and pKa
- 8.8 Properties of Buffers
- 8.9 Henderson-Hasselbalch Equation
- 8.10 Buffer Capacity
- 8.11 pH and Solubility
Unit 9: Applications of Thermodynamics
- 9.1 Introduction to Entropy
- 9.2 Absolute Entropy and Entropy Change
- 9.3 Gibbs Free Energy and Thermodynamic Favorability
- 9.4 Thermodynamic and Kinetic Control
- 9.5 Free Energy and Equilibrium
- 9.6 Free Energy of Dissolution
- 9.7 Coupled Reactions
- 9.8 Galvanic (Voltaic) and Electrolytic Cells
- 9.9 Cell Potential and Free Energy
- 9.10 Cell Potential Under Nonstandard Conditions
- 9.11 Electrolysis and Faraday’s Law
Course Content
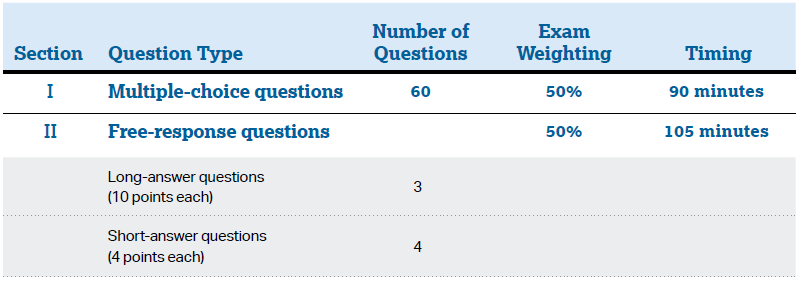
The AP Chemistry Exam assesses student understanding of the science practices and learning objectives outlined in the course framework. The exam is 3 hours and 15 minutes long and includes 60 multiple-choice questions and 7 free-response questions. Starting with the 2022–23 school year (spring 2023 exam), a scientific or graphing calculator is recommended for use on both sections of the exam. Students are provided with the periodic table and a formula sheet that lists specific and relevant formulas for use on the exam
Units Exam Weighting
Unit 1: Atomic Structure and Properties 7–9%
Unit 2: Molecular and Ionic Compound Structure and Properties 7–9%
Unit 3: Intermolecular Forces and Properties 18–22%
Unit 4: Chemical Reactions 7–9%
Unit 5: Kinetics 7–9%
Unit 6: Thermodynamics 7–9%
Unit 7: Equilibrium 7–9%
Unit 8: Acids and Bases 11–15%
Unit 9: Applications of Thermodynamics 7–9%